A number of antibacterial agents - cephalosporins, which include the antibiotic Ceftriaxone, were first discovered in 1948. Researchers have found that they are more resistant to the damaging effects of bacterial enzymes than, for example, penicillins. In 1964, scientists managed to isolate a pure substance from cell culture, which marked the beginning of the production of pharmaceuticals called the cephalosporin antibiotic group.
Material Content:
- 1 The composition of the antibiotic
- 2 Which group of antibiotics belongs
- 3 Pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics
- 4 Why is the drug prescribed for adults and children
- 5 Instructions for use Ceftriaxone in injections
- 6 During pregnancy and lactation
- 7 Can I drink alcohol while taking the drug
- 8 Drug Interactions with Other Drugs
- 9 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 10 Analogs
The composition of the antibiotic
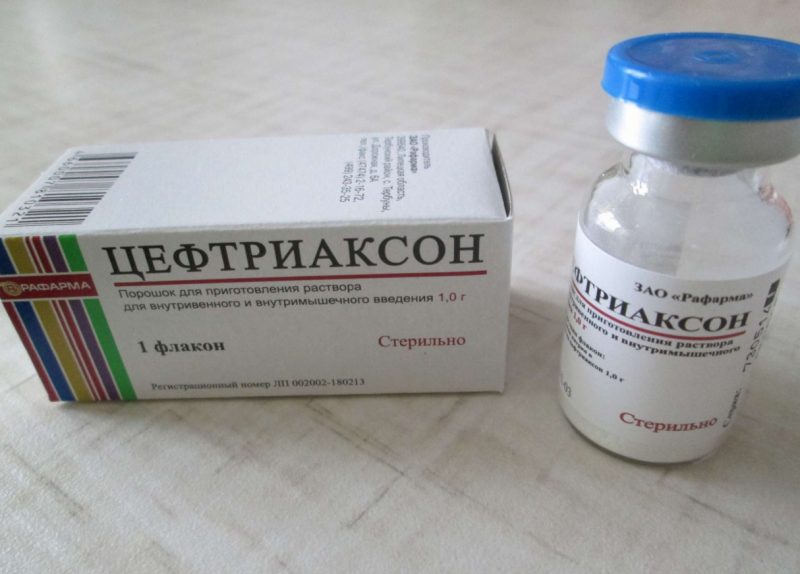
The antibiotic is ceftriaxone sodium. Its chemical formula is based on 7-aminocephalosporanic acid. The ampoules contain a completely sterile substance in the form of a white powder.
Which group of antibiotics belongs
Antibacterial therapy refers to a number of cephalosporins. This is a class of substances that are most resistant to enzymes produced by a bacterial cell. The higher the resistance, the greater the effect of the antibiotic on the pathogen.

In total, the class in question has five groups of compounds, otherwise they are called generations. This classification is based on the chemical structure of the substance itself and its degree of resistance to bacterial enzymes.According to this classification, ceftriaxone belongs to the third generation, which indicates its very wide spectrum of action and sufficient resistance (resistance) to β-lactamases (bacterial enzymes that destroy the drug).
Pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics
The drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. Studies have shown that its bioavailability does not change. An antibiotic tends to accumulate in the intercellular substance, so it penetrates equally well into all biological tissues and fluids.
Throughout the day, the medicine remains active, so each subsequent dose is administered only after 24 hours.
Up to 96% of the starting material binds to blood proteins. Moreover, this reaction has an inverse relationship. The higher the dosage of the drug, the less antibiotic will settle on albumin protein.
The highest drug content is determined in the blood after approximately three hours from the time of administration. The half-life of the body in adult patients is about 8 hours. In infants under the age of a crescent, the duration of this period of time can be extended by a day. The breakdown of the substance into metabolites in the body of the elderly is delayed and occurs in the range from 8 to 24 hours.
The antibiotic is excreted along with biological fluids - urine and bile. With kidney failure, it is more excreted by the liver and, conversely, with liver failure, the majority of the metabolites leave the body through the kidneys.
In the intestine, the active substance passes into a non-digestible form, and then is removed together with the processed food masses.
The action of the drug is to disrupt the synthesis of building components of the microbial cell wall. Thus, in his presence, irreparable structural changes occur in the bacterial cell, as a result of which it dies.
In other words, the drug has a bactericidal effect. It destroys existing bacteria and prevents the formation of new ones.
According to tests conducted outside a living organism, i.e., in vitro, the drug has a detrimental effect on:
- most strains of staphylococci (with the exception of Staphylococcus spp.);
- many gram-negative sticks, including salmonella, causative agents of meningitis, syphilis, intestinal and genitourinary infections;
- a number of pathogens and bacteria that are considered conditionally dangerous, propagating in an extremely oxygen-free environment (such as, for example, clostridia and bacteroids, which are part of the intestinal flora).
The results of the action of an antibiotic outside a living organism and specifically on a person or an animal may vary. Therefore, the conclusions drawn during the test in vitro are considered conditional. The sensitivity of each individual person is identified individually in a number of laboratory samples.
Why is the drug prescribed for adults and children
Ceftriaxone injections are prescribed for adults and children for the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms.

This circle includes:
- diseases of the intestinal tract and respiratory tract (especially pneumonia), including nose and throat;
- ear inflammation;
- genitourinary infections (for example, gonorrhea);
- pathological processes affecting the lining of the brain;
- kidney infections
- bacterial lesions of bones, joints and muscle tissue.
Injections are also prescribed as prophylaxis to prevent the development of bacterial infections in the postoperative period.
Instructions for use Ceftriaxone in injections
The injections are given intravenously or intramuscularly. For intramuscular injection of grams of powder, 3.5 ml of a 1% solution of Lidocaine is diluted. The needle is inserted deep into the gluteal muscle. At a time, no more than one gram of the drug can be administered in one muscle.
For intravenous administration, a solution is prepared. Ceftriaxone antibiotic should be diluted in proportion: gram of powder per 10 ml of sterile water.The medicine is injected into the vein very slowly for 2 to 4 minutes.
Injection is done once every 24 hours. The duration of treatment depends on the disease itself. Any therapy should not exceed a period of 14 days (more often, no more than 8 - 10 days).
For adults
All patients over 12 years of age are prescribed a single dose of 1 g. In case of impaired liver function, but maintaining kidney function, the norm does not decrease. In the opposite situation, while maintaining liver function, but with impaired renal function, the dose also remains the same.
With a decrease in the performance of both organs, it is necessary to carefully monitor the concentration of the drug in the blood.
- In severe cases, the medication rate may increase to four grams per day.
- In the treatment of gonorrhea, 0.25 g is administered intramuscularly at a time and once.
- For preparation before surgery, subject to probable bacterial infection, one or two grams of powder is administered to the patient one and a half hours before the start of manipulations.
The drug should not be simultaneously prescribed with aminoglycosides due to the unpredictability of the treatment result. Exceptions can be only complicated cases, for example, such as an extensive defeat by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, where it is a question of saving lives. In this situation, the indicated groups of drugs are administered in standard doses, but strictly separately.
For children
Children's dosage is calculated depending on age and weight. The minimum norm is 20 mg per kilogram of weight.
For newborns up to two weeks of age, the maximum amount of the drug per administration is 50 mg / kg. For all children over this age, flesh up to 12 years of age is prescribed no more than 75 mg / kg per application.
Exceptions are cases of bacterial meningitis. In this situation, at the initial stage of treatment, 100 mg of substance per kg of weight is administered to all patients under the age of 12, including newborns.
Immediately after it is possible to identify the pathogen and determine which drugs it does not have resistance to, the dosage is reduced to the standard. Treatment, depending on the pathogen, lasts from 4 to 14 days.
During pregnancy and lactation
At the stage of the first trimester of pregnancy, antibiotic treatment is contraindicated. In later periods, the question of the appropriateness of use is decided by the doctor.

Since the drug in question is able to be excreted together with breast milk, for the period of treatment it is worth considering the issue of excommunication or temporary cessation of feeding.
Can I drink alcohol while taking the drug

Since both substances and alcohol and the drug inhibit the function of the liver, their combined use is unacceptable. As a result of drinking alcohol during the treatment period, the development of toxic shock is possible - a severe liver damage.
Drug Interactions with Other Drugs
The drug in question is chemically incompatible with other agents containing calcium, as well as other drugs from the class of antibiotics. All these drugs can not be combined in one bottle, but must be administered separately.
You should know that the indicated remedy reduces the absorption of vitamin K, and also enhances the effect of drugs that reduce blood viscosity. Therefore, simultaneous use with anticoagulants can provoke the development of bleeding.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
Before deciding whether to conduct therapy, a patient is questioned to determine his hypersensitivity to cephalosporin antibiotics. In the presence of hypersensitivity, these drugs are not prescribed.

An absolute contraindication is the first trimester of gestation and the lactation period. Ceftriaxone during pregnancy at a later date is prescribed only after comparing all the risks and benefits.
The drug is relatively contraindicated:
- premature babies;
- newborns with signs of jaundice;
- persons with a history of intestinal lesions associated with the use of antibacterial agents;
- people with severe disabilities in the system of urination and blood formation.
With the introduction of the drug, patients may experience pain at the injection site, up to the development of thrombophlebitis. Immediately after the introduction of the substance, a burning tip of the tongue, a metallic taste in the mouth, extraneous odors, dizziness, malaise, and chills are felt.
Among the more severe reactions, skin manifestations of varying severity from simple rashes to complex dermatitis and erythema, as well as anaphylactic shock, were noted. As therapy continues, disruptions in the intestines, the development of mycoses of various localization, inflammation of the oral mucosa with the appearance of small sores, and all kinds of displacements in the blood picture can be observed.
For signs of overdose, emphasis is placed on relieving symptoms.
Analogs
There are a number of analogues containing the same active substance, but produced under other trade names: "Azaran", "Broadsef-S", "Lendacin", "Loraxon", "Medaxon", "Rofecin", "Stericef", "Torotsef" , "Cefaxone", "Cefson", "Ceftriabol", "Ceftrifin".
There are also drugs whose action is based on antibacterial substances of the same series that are similar in chemical structure and belong to the same group.
Third-generation cephalosporins are represented by drugs: Cefixime, Cefosin, and Cefoperazone.
Consider their comparative characteristics:
| drug name / characteristic | Cefixim | Cefosin | Cefoperazone |
|---|---|---|---|
| active substance | cefixime | cefotaxime | cefoperazone |
| release form | pills | powder for preparation of solutions | powder for preparation of solutions |
| dosage | 0.2 / 0.4 g | 0.5 / 1/2 g | 1 g |
| normal for adults | 0.2 g - 2 times a day; 0.4 g - 1 time per day | 1 g every 12 hours | 1 g every 12 hours |
| norm for children | 4 mg / kg - 2 times a day; 8 mg / kg - 1 time per day | 50-100 mg / kg every 12 hours | 50-200 mg / kg every 12 hours |
Indications, contraindications and side effects of drugs of the entire third generation are similar and do not need a separate description.
The discovery of cephalosporins, on the one hand, made possible therapy against penicillin-resistant pathogens. On the other hand, it increased the likelihood of superinfection.
As antibiotic aggressiveness increases, more and more microorganisms that are resistant to new types of drugs appear. This fact is especially worth considering when prescribing Ceftriaxone for children, since it is in small patients who are most likely to encounter all kinds of pathogens.