Chlorhexidine is the most famous antiseptic that has been used in medicine for more than half a century. This tool is widely used due to its pronounced antimicrobial activity, the variety of dosage forms and affordable cost. Chlorhexidine, the use of which has virtually no contraindications, is used in surgery, gynecology and otolaryngology.
Material Content:
Release forms and composition (active substance)
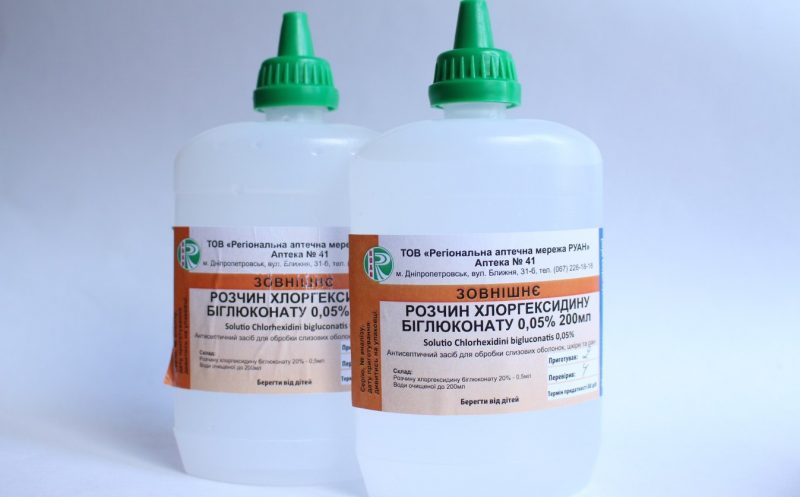
The active substance of an antiseptic is chlorhexidine bigluconate. The drug is available in different dosage forms and dosages.
In pharmacies are presented:
- vaginal suppositories;
- solution for local processing;
- gel for skin treatment;
- alcohol spray.
Vaginal suppositories are available in two dosages - 8 and 16 mg of the active substance in one candle. In pharmacies there are candles under various commercial names - Chlorhexidine, Hexia, Hexicon, Hexigin-M, etc.
The solution contains 0.05% of the active substance, a solution for rinsing the mouth and throat is also available in a dosage of 0.2 and 0.1%. The gel contains 0.5 g of chlorhexidine in 100 g of the drug and is intended only for the treatment of the epidermis. Alcohol spray also contains 0.5 g of active ingredient per 100 ml of the drug, it is used mainly for antiseptic treatment of hands.
An antiseptic solution is used to disinfect work surfaces and medical devices used for diagnosis.
Instructions for use of chlorhexidine
Instructions for use of the drug depend on the chosen form, concentration and indications. Means for external use is used in various purulent-septic processes, for the treatment of burns and wound surfaces. In dermatology, the antiseptic gel Chlorhexidine is also used.
Vaginal suppositories are prescribed for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis caused by bacteria sensitive to the drug, as well as to prevent infection by infections transmitted through unprotected intercourse.
Chlorhexidine is active against a number of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis. Vaginal suppositories are prescribed for prophylaxis before surgery or the installation of an intrauterine device.
Solution for local and external use
It is advisable to use chlorhexidine in the form of a solution in the following cases:
- wounds and abrasions;
- burns;
- diseases of the ENT organs;
- gynecological and urological diseases;
- STD prevention
- diseases of the teeth and gums.
For these purposes, use a solution in a concentration of 0.05, 0.2 and 0.5% of the active substance. The solution is used to rinse the mucous membranes, application processing of the skin, irrigation of the urethra in men and women, douching.
To treat damaged skin, a small amount of solution (5-10 ml) is applied to a cotton swab, which is pressed onto the epidermis for several minutes. Processing should be carried out up to three times a day.
The solution is used to gargle with inflammatory diseases, it is also prescribed for the treatment of the oral cavity with gingivitis, stomatitis and periodontal diseases. Rinse chlorhexidine should be used three times a day.
Note! The use of a highly concentrated solution for treating the oral cavity can lead to darkening of the enamel, therefore it is recommended to use the drug in a concentration of 0.2%.
To prevent sexually transmitted diseases, a few milliliters of the solution is injected into the urethra or vagina immediately after unprotected intercourse and left for a couple of minutes. The drug is effective only if used no later than 2 hours after coition. After the procedure, you should not urinate for two hours. In general, chlorhexidine in gynecology is more often used in the form of suppositories.
Alcohol spray for external use
Alcohol solution is used to treat skin of hands, medical instruments. It can also be used to treat the external genitalia, but getting on the mucous membranes should be avoided, as there is a strong burning sensation.
To process work surfaces and tools, spray is applied to a sponge or rag, and then wipe the item for several minutes. Hand disinfection is carried out as necessary, but no more than 4 times a day, since the ethanol in the composition dries the skin.
During pregnancy and lactation
An antiseptic is not forbidden to use during pregnancy and lactation. Moreover, suppositories with chlorhexidine in the composition are one of the commonly prescribed agents for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy. The dosage and duration of treatment in this case is selected by the doctor individually.
During lactation, suppositories can be used without restrictions, according to the instructions, since the active substance does not penetrate into breast milk. The solution should not be used to treat nipples during lactation.
Drug interaction
The drug cannot be used with soap and hygiene products containing sodium lauryl sulfate (foaming agent). When using suppositories, washing the external genitalia with soap is not prohibited, but you should refrain from additional douching until the end of the course of treatment.
Topical antiseptics should not be used with iodine-containing agents.The product is also not compatible with sulfates, borates and carbonates.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
Contraindications to the use of an antiseptic in any dosage form:
- children under 6 years old;
- dermatitis;
- epidermal viral diseases;
- allergic skin rashes.
An antiseptic can not be used with individual intolerance to the active substance. The use of chlorhexidine in children should be agreed with your doctor.
The drug is not intended for use in ophthalmology and internal administration.
In case of ingestion, immediately rinse the stomach. Reception of a solution in large quantities (over 300 ml) can be fatal due to acute renal and hepatic failure.
With prolonged use of the drug in the form of a solution or gel, symptoms of an allergic reaction, itching and peeling of the skin may appear.
Side effects:
- allergic rash;
- dryness of the epidermis;
- itching at the injection site of the suppository;
- photosensitivity of the skin.
In the vast majority of cases, the drug is well tolerated by the body. If chlorhexidine-based drugs are used according to the instructions, the risk of side effects is minimal.