Each country has its own vaccination calendar. When compiling it, the prevalence of infections in a particular area and the availability of medical preparations at the disposal of specialists are taken into account. Such a calendar is subject to change. For example, if a new, effective vaccine is being developed or there is a risk of epidemic.
Material Content:
- 1 What is preventive vaccination?
- 2 Vaccination calendar for children under 1 year
- 3 What vaccinations do you need to get up to 3 years
- 4 Vaccination plan from 3 to 14 years
- 5 National vaccination calendar: concept and features
- 6 The vaccination procedure for citizens within the national calendar
- 7 Vaccination schedule for adults
- 8 Vaccine classification and methods of administration
- 9 What entails the lack of preventive vaccination
- 10 Preventive vaccination in kindergarten
What is preventive vaccination?
Preventive vaccinations are an important procedure that allows a person to avoid infection with various diseases. Vaccines are made on the basis of constituent viruses, which are the most dangerous for modern people. Of course, only the minimum dose of the bacterial components is included in the serum, which does not overload the immune system, but at the same time allows the body to remember the “guest” and be ready to deal effectively with it during a real infection.

Faced with a dangerous virus after the vaccination is carried out on time, a person will either avoid infection or cope with the disease easily, quickly and without any special complications.
Some vaccines are included in the list of free medical procedures for children and adults. This is a necessary measure to prevent the development of large-scale epidemics of various diseases.
A vaccination plan is prepared by experienced infectious disease specialists. In it, doctors must note the recommended dates for the procedures under discussion.To maximize the effectiveness of vaccinations, you must adhere to the plan drawn up by doctors.
Vaccination calendar for children under 1 year
In Russia, people receive their first vaccines in the hospital shortly after birth. Within a day after birth, the baby is vaccinated against hepatitis B. This urgency is explained by the high risk of contracting a dangerous virus in the country. This is the first of a series of treatments. The vaccine is repeated at 1 and 2 months, at 6 months, at 12 months and older. Typically, this vaccination option is well tolerated by a healthy child.
Only in rare cases, the baby can rise in body temperature or allergy. Vaccination of premature babies and suspected their HIV infection is prohibited.
If the child was born without deviations and any health problems, then while being in the hospital, he is given a vaccine against tuberculosis. Further, the child will face other preventive procedures aimed at preventing tuberculosis and controlling the threat of the disease. For example, these are Mantoux tests.
A large number of vaccinations are given to a child aged 3 months. This is a vaccine against tetanus, pertussis, diphtheria, polio, hemophilus bacillus. The procedure is also repeated at 5 and 6 months, and also after a year. Among vaccinations for children up to 1 year old, the option against rubella, measles and mumps should be noted. These vaccines are given to the baby immediately before the first birthday.
One of the most difficult among the required vaccinations is the compound DTP. It protects the child at the same time from tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria. In the first year of life, the crumbs are immediately given three such vaccinations. And at an older age, revaccination is performed so that the antibodies in the patient's body retain their strength.
It is important that only completely healthy children attend vaccination procedures. Only in this case, the vaccine will not harm the body of the child. Vaccination is a voluntary procedure. But parents should remember that during the epidemic and under certain other conditions, only vaccinated children have the right to attend kindergarten and other educational institutions in order to avoid the spread of viral infection.
If a child attends children's groups, the pediatrician may recommend a flu shot. It is held every fall and also prevents a massive epidemic of the disease. Such vaccination is allowed for children older than 6 months.
What vaccinations do you need to get up to 3 years
Up to 3 years, the list of compulsory childhood vaccinations primarily includes revaccination of the compound DTP. Usually it is put to the child at 1.5 years.
If the baby's teeth are actively being cut, he feels bad during the period recommended for vaccination, then parents can independently adjust the period of vaccinations by choosing the most comfortable for their child.
At 1.5 years of age, a vaccine is also given against polio and hemophilic bacillus. Some parents choose for their baby foreign analogues of domestic vaccinations (most often - DTP). In this case, one vaccine can include all dangerous infections at once. So, the popular Pentaxim will protect the child immediately from 5 common childhood diseases. Including polio.
True, unlike domestic vaccine options, parents will have to pay for foreign-made drugs on their own. Free of charge they are assigned to small patients only in rare cases. For example, if a child has a serious allergy to the components of a domestic vaccine.
Vaccination plan from 3 to 14 years
A lot of vaccinations will have to be given to a child up to 14 years old. If the patient receives the last hepatitis B vaccine at 1 year old, then the next hepatitis B vaccine will be recommended at 6–8 and 11–13 years old. For example, a vaccination may be given in front of a school.
The second DTP revaccination is recommended for a child aged 6-7 years. It is also often put in preparation for school.The last vaccine was recommended at the age of 14. It is called ADS and does not include pertussis component.
The vaccine against tuberculosis is repeated two more times. BCG is re-established at 7 and 14 years old. And against polio - only at 14 years old.
The rubella, mumps and measles vaccine is given to a child aged 6 years. And from 11 years old - exclusively against rubella. It must be repeated every 5 years and thereafter. Under 18 years old - for boys and up to 25 years old - girls.
Every year, a child can get a flu shot. But this is a voluntary procedure that parents record it on their own.
National vaccination calendar: concept and features
The modern national vaccination calendar is an official document approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. It spells out all vaccinations that are given to citizens free of charge (without fail). These procedures are regulated by the compulsory medical insurance program for Russians.
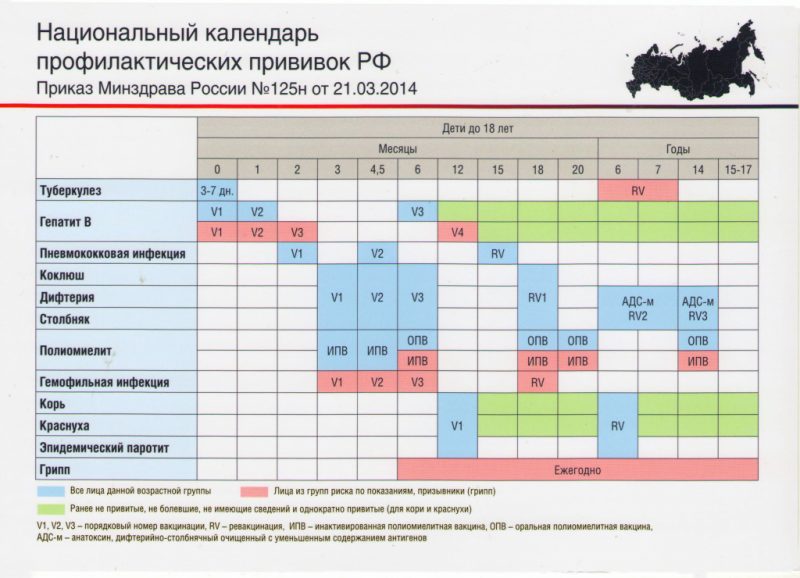
The document under discussion consists of 2 parts at once. The first half of the calendar offers a list of recommended vaccinations against the most common infections. In the second half, vaccines are indicated, which are indicated in some risk groups and during periods of epidemic. So, for example, adult citizens who are constantly working with live cultures, on harvesting, with soil, are recommended vaccination against tularemia. And to employees of veterinary clinics - against rabies.
Such a calendar can be studied by everyone. It provides information on each vaccination of interest to the user: its name, purpose, duration of vaccination and other important information are indicated. This document is followed by all medical professionals.
The latest improvements to the Russian vaccination calendar were made in the spring of 2017.
The vaccination procedure for citizens within the national calendar
Vaccinations for adults and children in Russia are carried out strictly according to the national calendar. As already noted above, the first vaccine is given to a child soon after birth - on the first day of his life. The vaccine is given right in the hospital.
Further, parents should bring their child to a medical institution on their own, following the vaccination schedule. The pediatrician and nurse supervise the visit to the procedure. If parents refuse to vaccinate their child, they will need to write a complete refusal of vaccinations or to confirm in writing the schedule shift. For example, related to health problems in a child.
A special procedure for vaccinations must be observed for children born to HIV-infected mothers.
Vaccines are often given to adult patients during professional examinations. Before vaccinating a patient, he should be examined by a medical assistant and give consent to the procedure.
Vaccination schedule for adults
Adult patients are much less likely to attend prophylactic vaccination procedures. After all, you have to find out about the dates of their conduct on your own and find time to visit a medical institution.
In adulthood, it is necessary to undergo a revaccination procedure against tetanus and diphtheria every 10 years (from 18 years). The vaccine against viral hepatitis B is repeated every 5-7 years until the patient reaches 55 years of age.
Measles vaccine is given at age 25. Further revaccination is not required. But the rubella vaccine should be repeated for adult women from 25 to 45 years. This is especially true for patients planning a pregnancy. Revaccination is carried out every 10 years to maintain the activity of immunity. Men do not need a procedure.
A tetanus / diphtheria vaccine is indicated after 24 years. Her revaccination is carried out once every 10 years.
If there are children in the house, then vaccination against chickenpox becomes desirable. This applies even to those cases when a person underwent the procedure in childhood.
Patients with high sugar levels and chronic diseases of the internal organs are shown a pneumococcal infection vaccine.
Vaccine classification and methods of administration
All vaccines are divided into living and dead (inactivated). The first allows you to create a strong immunity against certain viruses, which will persist for a long time. The composition of this vaccine includes "assorted" strains of weakened microorganisms. They are used against polio, tuberculosis, measles and some other diseases. The disadvantages of this type of vaccine are the difficulty in combining and selecting the exact correct dosage, the categorical prohibition of use in immunodeficiency, the complexity of their storage and transportation.

Killed vaccines are grown on purpose. In the process, structural proteins are minimally damaged, therefore processing is additionally applied, for example, with formalin or alcohol. This type of vaccine acts for a short time, can cause allergies and poisoning of the body. But they are easy to combine and dose, can be used even with immunodeficiency of the patient.
Vaccines are classified by the method of their introduction into the body. Recently, the needleless (cutaneous) method has remained particularly popular, but so far costly. The medicine is injected with a powerful warm stream through the skin. In this case, the patient does not experience pain.
Intradermal options are introduced using a needle. Usually in the shoulder or forearm. This is a BCG vaccine, as well as vaccinations against plague, tularemia, anthrax and other diseases. With subcutaneous vaccination, the drug is injected into the side sections of the abdomen, under the scapula, in the shoulder, and thigh. For example, DTP. Intramuscular injection is carried out in the buttocks (against hepatitis B).
Aerosol and oral methods can preserve the integrity of the skin. Drugs in the form of tablets or liquids are administered through the mouth or nose. These are vaccinations against measles, flu, whooping cough, tetanus, botulism, plague and other diseases.
What entails the lack of preventive vaccination
If parents refuse to vaccinate their child and / or attend an important procedure on their own, they should be aware of the possible consequences.
If there are no vaccinations, the following situations may occur:
- Hospitals, kindergartens, schools and other similar institutions will be inaccessible to the patient for the period of the epidemic or in case of its threat.
- He will not be allowed into some countries of the world.
- A citizen will be dismissed from work or not accepted for it if the job involves frequent encounters with infections.
Preventive vaccination in kindergarten
For young patients, vaccination may be in group form. For example, in kindergarten.
At the same time, specialists with appropriate vaccines come to the preschool institution. And nurses in the kindergarten make lists of children who need and are allowed a procedure.
Vaccinations under such conditions are also given exclusively with the consent of the baby's parents. The family can write a written refusal of the procedure and refer it to the kindergarten nurse.