“Cortexin” is a nootropic drug classified as a protein bioregulator. This medication helps to normalize brain processes, protects tissues from toxins, eliminates seizures and has a general therapeutic effect on the central nervous system. According to the instructions for the drug, for children it can be used from birth. Consider why injections with this agent are prescribed, and how to use the drug correctly.
Material Content:
- 1 Release forms and composition
- 2 Pharmacological action, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- 3 What is the drug prescribed for?
- 4 Instructions for use Cortexin in injections and tablets
- 5 During pregnancy and lactation
- 6 Special instructions for taking the drug
- 7 Drug interaction
- 8 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 9 Analogs of a nootropic drug
Release forms and composition
"Cortexin" is made on the basis of lyophilisate. This enzyme is a concentrated extract of protein fractions that have been dried by a special technique. They are extracted from the brain tissue of pigs and cattle.
The compound looks like a white or yellowish suspension, packaged in bottles. Before use, the powder is diluted with special solutions for injection.
The medicine prescribed for adults is presented in ampoules of 10 ml with a content of 0.005 g of the drug. And Cortexin, used in pediatric practice, is placed in containers of 3 or 5 ml, with the same concentration of lyophilisate.
Vials of powder are placed in contour packs with cells, which, in turn, are laid out in cardboard boxes. Each tool is accompanied by an annotation containing a detailed guide to its use.
The medicinal composition retains the desired properties for 3 years from the date of production, but only if stored in a dark and dry room at a temperature of 2 to 20 ºС.
"Cortexin" refers to prescription drugs, and it is impossible to freely purchase it in a pharmacy. This requires a prescription from a doctor.
Attention! The drug is available only in the form of a powder for the preparation of injection solutions. Other forms, such as tablets or capsules, do not exist. If other types of Cortexin are on sale, it is likely that these are fakes.
Pharmacological action, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Lyophilisate promotes activation of neurons in the brain, due to which its ability to transmit impulses between different departments increases. At the same time, it is able to suppress convulsive activity, as well as normalize the balance of amino acids, serotonins and dopamines.
The drug has a complex effect on the body.
As a result of its use, the effects of the following types are observed:
- Nootropic. Patients improve memory and ability to concentrate, as well as increase resistance to stress.
- Anticonvulsant. In the presence of painful foci in the brain, the drug helps to suppress their activity.
- Antioxidant. Active substances slow down the oxidation of lipid compounds, and also protect brain tissue from exposure to toxin. In addition, increased cell viability even with oxygen starvation.
- Neuroprotective. The medication helps protect neurons from the effects of components such as calcium ions and free radicals. In addition, Cortexin is involved in metabolic processes and helps to improve the general condition of the nervous system.
Since the drug has a polypeptide structure, it easily penetrates the barrier between the nervous and circulatory systems. The decay of the dominant component of the drug takes no more than 3 minutes, for this reason it is not possible to determine the pharmacokinetic properties. Doctors have no data on how quickly peptide residues are absorbed, and how their distribution in the body occurs. It is also not established how the compound is excreted, and where its metabolism is made.
What is the drug prescribed for?
"Cortexin" is indicated for use in the detection of the following conditions:
- disorders in the central nervous system that occurred on the background of bacterial, viral or infectious attacks;
- diseases that occur against the background of cerebrovascular accident;
- TBI of varying severity and the complications that they caused;
- diffuse lesions of brain cells of various etiologies;
- cerebral and autonomic disorders.
In complex therapy, the drug can be prescribed for epilepsy and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in acute or chronic form, regardless of their origin.
In pediatric practice, a drug is used in the presence of such disorders in a small patient:
- mental and speech development delays;
- various lesions of the central nervous system;
- cerebral palsy;
- previous injuries and stresses;
- increased irritability and nervousness;
- decreased memory and concentration.
Cortexin is allowed to be used from birth, and it is also prescribed for premature babies when there are good reasons for this. The main indications in this case include birth injuries, neuroinfection, and birth hypoxia.
Instructions for use Cortexin in injections and tablets
The drug is able to provoke overexcitation of the nervous system, therefore, it should be administered in the morning 1 time per day. Usually, the course of treatment lasts 10 days, but if necessary, can be extended or repeated after some time. As a rule, the interval between courses is from 3 to 6 months.
Cortexin for children
The dosage for the child is planned based on his body weight. If the patient weighs up to 20 kg, 0.5 mg of the substance per 1 kg. For older children, an increased dose is prescribed, which is determined by the attending physician. Most often it is 10 mg for single use.
The optimal course is 10 injections. If on one day the injection was missed, the next time only a single dose can be administered, pricking a double volume is prohibited.
Adult use
Adult patients are prescribed 10 mg of a substance for a single injection. The duration of the course is the same as for children. But the pattern changes if the patient has suffered an ischemic stroke. Here, individual dosages are used, and the duration of therapy depends on the patient's condition.
Attention! An opened ampoule with unused powder must not be stored. In the case when the patient needs a lower dosage, the remaining drug must be disposed of.
During pregnancy and lactation
Doctors have no genuine and convincing data on how dangerous “Cortexin” can be for the body of a pregnant woman and an unborn baby. Therefore, during the gestation period, he is not prescribed.
The ban applies to nursing mothers. But if there is an urgent need for treatment with this drug, the baby is transferred to artificial nutrition throughout the course of therapy.
Resuming feeding is allowed only 24 hours after the last injection, if lactation is maintained.
Special instructions for taking the drug
Since the medication is presented in powder form, it is important to know how to breed it.
You can do this with such solutions:
- procaine 0.5%;
- novocaine 0.5%;
- saline 0.9%;
- water for injection.
For one bottle of medicine, from 0.5 to 1 ml of liquid is required. This dosage is intended for adult patients, and 2 ml of solution is added to the syringe for the child. At the same time, doctors recommend using water, since novocaine can cause allergic reactions. And to prevent the appearance of foam, when taking medicine into the syringe, the needle must be placed on the wall of the ampoule.
Attention! "Cortexin" during injection is used only as a single drug, it is unacceptable to combine it with other formulations in the same syringe.
Drug interaction
"Cortexin" is combined with other groups of medicines, with the exception of drugs with a peptide structure. No other cases of pronounced interaction were recorded.
Due to this feature, the drug is prescribed in complex therapy, combining with those means that the attending physician selects.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
The main prohibitions on the appointment of "Cortexin" are the period of pregnancy and lactation, as well as intolerance or other acute reaction to the active substance.
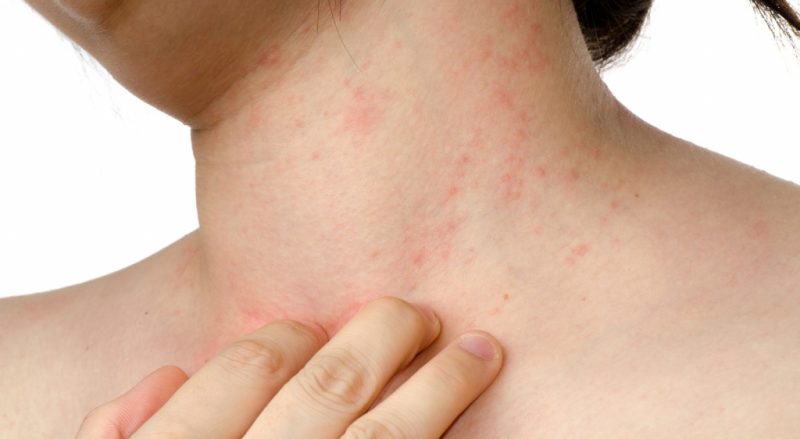
The drug causes side effects extremely rarely, these may be such symptoms:
- redness at the injection site;
- different manifestations of allergies.
According to patients, such effects, if they appear, then disappear rather quickly.
There were no cases of drug overdose, we can only assume that in such a situation the symptoms described above will be more pronounced.
Analogs of a nootropic drug
If you want to choose an analogue of "Cortexin", from the funds presented in the same dosage form, it can be replaced with such drugs:
- "Nucleo CMF Forte";
- “Armadin”;
- "Nicomex";
- Mexiprim;
- “Cytoflavin”;
- "Neurotropin."
When an analogue is selected in tablet form, it is advisable to use such means:
- "Rilutec";
- "Cytoflavin";
- Armadin
- glutamic acid.
There is another analogue of the drug, and patients often ask the question, which is better, Cortexin or Cerebrolysin. According to the results of studies, it was found that they have a similar effect, but the effectiveness of Cortexin is much higher.
In addition, the designated drug can be used for children from birth, while Cerebrolysin is prescribed for babies only in special cases. But at the same time, patients note that Cortexin injections are more painful than its counterpart.
In any case, the final decision regarding the choice of drug is made by the attending physician.
- Inna