The medical term otitis media is a generalization. So called infectious and inflammatory processes affecting the auditory organs. They are external, medium and internal, depending on localization. This article describes the features, causes, symptoms and treatment of otitis media, as well as a list of measures to help prevent the disease.
Material Content:
Otitis media: causes of the disease
Otitis media can occur for various reasons related to the individual characteristics of the patient, the state of his immune system and environmental influences.

The following factors can provoke the disease:
- infections affecting the auditory organs;
- traumatic injuries of the auricles;
- diseases of the nasopharynx;
- reduced immunity;
- violation of the rules of hygiene of the auditory organs;
- hypothermia.
At risk are people who are allergic and have undergone surgery involving the oral and nasal cavities.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Inflammation of the middle ear is manifested by various symptoms, depending on the form and stage of the disease.

Most often, the following symptoms occur:
- the appearance of sharp, shooting pains in the auricle;
- general malaise and weakness;
- headaches accompanied by nausea;
- a feeling of stuffiness in the ear, which occurs due to accumulation of fluid;
- short-term hearing loss;
- purulent discharge from the auricles, indicating the development of purulent otitis media;
- the presence of blood in the separated fluid, which happens with severe forms of the disease and indicates damage to the eardrum.
Attention! Otitis is a serious disease, and at the first signs of an illness it is necessary to immediately seek medical help, otherwise the occurrence of formidable complications is not excluded.
Types and stages of otitis media
Otitis media is characterized by inflammation affecting the tympanic cavity. The disease proceeds in several stages, and each of them has its own symptoms.
Acute otitis media
The initial form is called "catarrhal acute otitis media."

During this period, the liquid gradually accumulates, which makes itself felt through such manifestations:
- pain in the ears, extending to the jaw, temple or neck;
- ringing or tinnitus;
- feeling of stuffiness and pressure inside the body.
Sometimes the initial stage of the disease proceeds against a background of elevated temperature, this indicator can reach 39 ° C. If it was not possible to suppress the disease in its infancy, it proceeds to the next stage, which is called purulent or performative.
Purulent otitis media
At this stage of the development of the disease in the ear cavity, purulent discharge forms and accumulates, which press on the membrane and cause pain. They disturb the patient almost constantly and intensify when swallowing or careless turning of the head.

In addition, pus starts to stand out from the ear, the temperature rises and hearing is periodically worsened. This stage lasts from 2 to 3 weeks, and if the patient has not received proper treatment, otitis media can become chronic.
Chronic otitis media
Untreated or chronic otitis media is characterized by the appearance of adhesions in the ear cavities, which arise due to the accumulation of fluid. Such formations impede the normal functioning of the auditory organ, as a result of which hearing is reduced, quite often there is tinnitus and dizziness.
And also at this stage, mucous secretions are frequent, which can be permanent or episodic.
Diagnosis of the disease
Otitis can be recognized by visual inspection. The doctor makes such a diagnosis if there is redness in the auricles, indicating an inflammatory process, and the patient complains of pain and general malaise.
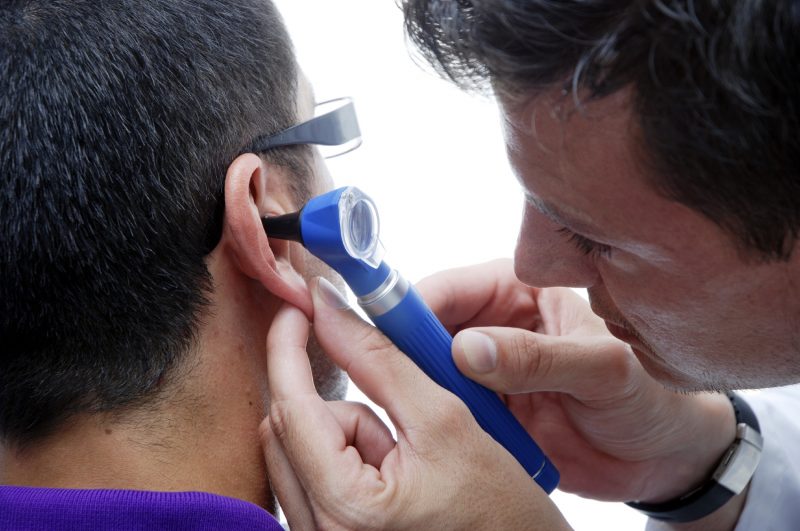
If, in addition to the indicated symptoms, hearing loss and dizziness are observed, the following diagnostic measures are necessary:
- hardware examination of the auricle;
- measurement of pressure inside the ear using special equipment.
In situations where there is a suspicion of complications, such measures are prescribed:
- CT and MRI of the brain and temporal bones;
- X-ray
- consultation of a neurologist and optometrist.
Attention! A doctor can prescribe an adequate treatment for otitis media after making an accurate diagnosis. Self-healing is strictly prohibited.
Treatment of middle ear inflammation in adults
Treatment of inflammation is carried out comprehensively and includes the use of various drugs, as well as physiotherapeutic effects.
Drops with otitis media
For topical administration, drops are prescribed that are required to be instilled into the ears several times a day.
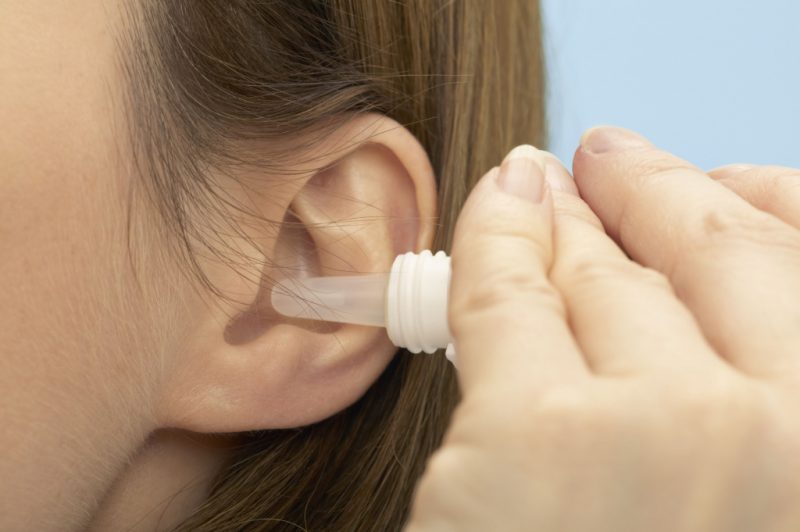
In the process of treatment, drugs are used to achieve the following results:
- restore the microflora of the auricles and destroy pathogenic bacteria;
- block the inflammatory process;
- relieve pain.
The maximum effect of these medicines is achieved if they are used comprehensively.
Antibiotics and other drugs
With otitis media, antibiotics are prescribed both in the form of drops, and in the form of tablets and injections. These medicines are necessary in order to stop the inflammatory process and destroy the pathogenic microflora.
In addition, drugs of the following groups are prescribed:
- analgesics to relieve pain;
- glucocorticoids, for swelling;
- means for expanding blood vessels, allowing to expand the ear canal;
- antihistamines, if otitis media is allergic in nature;
- antipyretic drugs at elevated body temperature.
In addition, it will be necessary to take medicines that restore the normal intestinal microflora, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes to support the immune system.
Treatment with folk remedies
You can increase the effectiveness of the treatment with the help of traditional medicine.
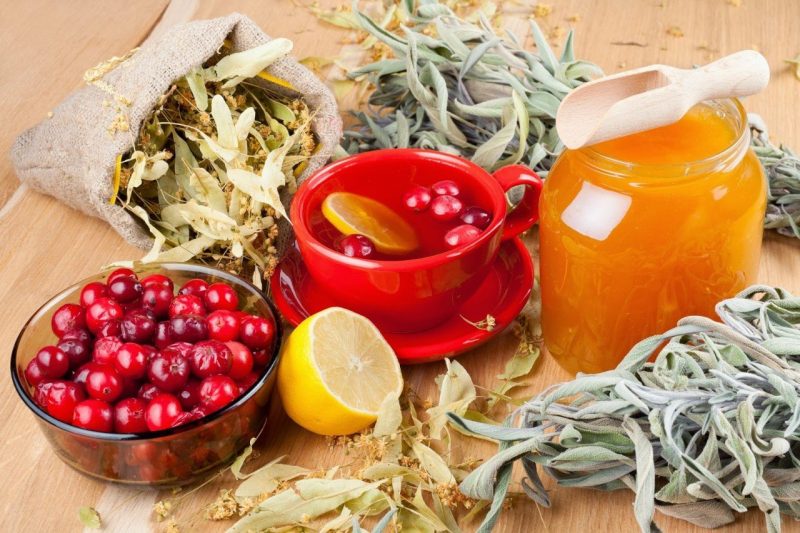

The most effective are:
- A mixture of pomegranate juice and honey. These components are taken in equal amounts and heated until the honey melts. After this, the product will need to be cooled, dipped in a cotton swab and lubricate the ear canal.
- Walnut or plantain leaves. Of these, you need to squeeze the juice, mix with water in a ratio of 1: 1 and instill 2-3 drops in the ear twice a day.
- Propolis. Tincture is moistened with cotton and introduced into the ear canal. Tampons will need to be changed twice a day.
- Dry leaves of medicinal melilot and chamomile flowers. These components will need to be mixed in equal proportions and brewed in a thermos 2 tablespoons of the composition, pouring a glass of boiling water. Then in the resulting infusion you need to dip a cotton swab and enter into the ear canal.
- Elderberry flowers. The dried inflorescences are scalded with boiling water and placed in a small bag, and then applied to the ear. The procedure is repeated several times a day.
Attention! Warming should be carried out only with the permission of the attending physician, since in some forms of otitis media, thermal exposure is contraindicated.
Physiotherapy for otitis media
Physiotherapeutic effect is effective in the treatment of many diseases, including otitis media.
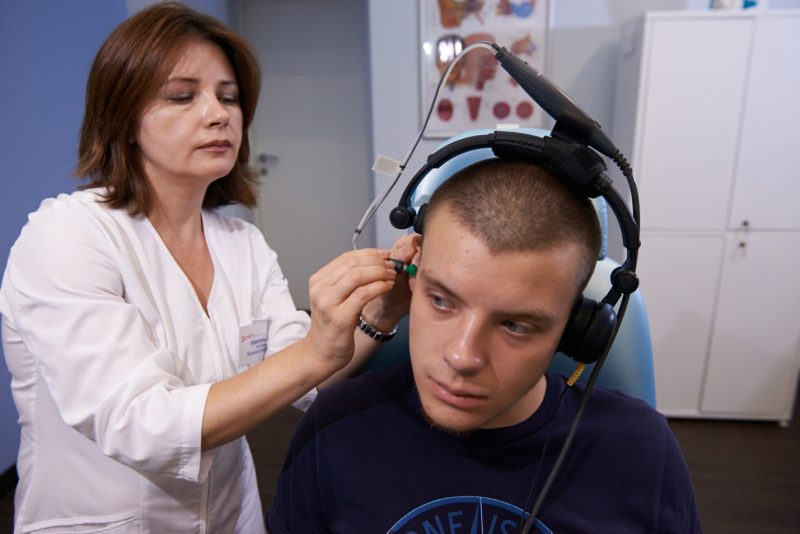
For such problems, the following procedures are prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- quartz tube;
- Ural federal district;
- phototherapy.
These manipulations allow you to stop inflammation, destroy the pathogenic microflora and relieve pain, as well as strengthen local immunity.
Possible complications of the disease
With proper treatment, in most cases, complications do not arise.

But in situations where medical care is provided incorrectly or out of time, this can lead to the development of such conditions:
- Mastoiditis. This disease is characterized by purulent formations in the mastoid process and tympanum. In the absence of proper treatment, the accumulated masses break through the eardrum and cause disturbances in the brain.
- Purulent meningitis. In such cases, the lining of the brain becomes inflamed, and its tissue itself remains intact. Failure to take action on time will result in death.
- Abscess of the brain. Breaking through the eardrum into the brain, pus is localized in its membranes, causing various injuries in the tissues.
- Venous sinus thrombosis. With these conditions, the blood circulation in the brain is disturbed, which leads to oxygen starvation, which can lead to severe violations in the work of various organs and systems.
To avoid such troubles, it is necessary to seek medical help at the first sign of otitis media and strictly observe all the appointments of the attending physician.
Prevention of otitis media
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure.
To avoid otitis media, you will need to adhere to the following rules:
- avoid hypothermia of the auditory organs;
- observe the principles of personal hygiene;
- avoid traumatic damage to the ears;
- take vitamins and drugs to enhance immunity;
- timely treat ENT diseases;
- at the slightest violation seek professional help.
It cannot be argued that by observing the above rules, one can completely avoid otitis media.But the listed preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of this dangerous disease and its serious complications.