According to competent sources, every fifth inhabitant of the Earth suffers from anemia to one degree or another. This is due to many reasons, including a violation of the absorption of iron ions in the digestive system. Severe cases of iron deficiency anemia require artificial replenishment of the concentration of iron in the body with the help of drugs. Iron preparations for low hemoglobin in adults can be used in tablet or parenteral form.
Material Content:
Causes and signs of iron deficiency
Normally, the amount of iron in the human body is approximately 4-4.5 grams. Moreover, there is a concept of its physiological loss. Women lose nutrient during pregnancy, menstruation, lactation. It is also excreted in feces, sweat and exfoliating skin cells. To compensate for these losses, men need about 10 mg of iron per day, women need about 18 mg. Pregnant women should consume 38, and lactating 33 mg of nutrient per day. With reduced consumption, iron deficiency anemia develops.
In addition to the above, low iron in the blood is noted in the following pathological conditions:
- chronic bleeding (gastrointestinal, from hemorrhoidal nodes, uterine, from tumors, etc.);
- resection of the stomach or part of the intestine;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract (enteritis, gastroenteritis, colitis, gastroduodenitis);
- chronic renal failure;
- hemosiderosis of the lungs;
- violation of the synthesis of transferrin - a protein that carries iron to the bone marrow.
A decrease in the concentration of iron ions leads to the appearance of certain clinical symptoms. Iron deficiency anemia is characterized by pallor of the skin, sagging and dry skin, dysphagia, hypotension, tachycardia. During laboratory examination, the patient also noted a reduced level of hemoglobin, a decrease in the average volume of red blood cells, a decrease in the hemoglobin content in the red blood cell.
Note: the following indicators are considered normal: Hb (hemoglobin) - in men - 130-160 grams / liter, in women - 120-140 grams / liter. The average volume of red blood cells is 80-100 micrometers 3. The hemoglobin level in the red blood cell is 25-32 picograms.
Low iron with normal hemoglobin
In some cases, a decrease in iron levels is possible without the development of anemia.
The fact is that in the human body the substance is present in three forms:
- cellular iron (as part of hemoglobin);
- extracellular iron (transport proteins, free plasma trace element);
- iron reserves (ferritin, hemosiderin).
Directly on the level of hemoglobin affects only the indicator of cellular iron. A decrease in extracellular nutrient numbers does not immediately lead to anemia. It is worth noting that in this case, the hemoglobin indicators are still reduced, but this happens with some delay.
Low iron with normal hemoglobin is detected mainly in patients with impaired mineral metabolism. In addition, pathology can occur after hemodialysis, forced diuresis and other procedures associated with the stimulation of urination or defecation. Serum iron is considered to be low, which is below the level of 9 micromol / liter. At the same time, erythrocyte indices decrease, which indicates the imminent development of anemia.
Iron preparations with low hemoglobin

Patients with iron deficiency anemia should receive at least 20-30 mg of the missing nutrient per day. It is practically impossible to provide a similar amount of a substance by its ingestion with food (especially against the background of impaired absorption from the digestive tract), therefore, the component is administered in the form of drugs. During normal bowel and stomach function, iron supplements can be taken by mouth (orally), in combination with Vitamin C or folic acid. If absorption in the gastrointestinal tract is impaired, medications are administered intramuscularly. Medicines may contain a divalent or trivalent type of iron.
Read also: the norm of hemoglobin in men by age in the table
Medicines with ferrous iron
Preparations containing ferrous iron are highly bioavailable, therefore their use is preferred. As a rule, the funds of this group are prescribed in tablets. Their intake is accompanied by such side effects as a taste of the metal in the mouth, nausea, and a decrease in appetite. Assimilation of the drug occurs under the action of appopheritin, which, combining with metal ions, turns into ferritin and enters the red bone marrow.

The most famous drugs with Fe2 + include:
- Iron sulfate - 325 mg (1 capsule) are prescribed 2 times a day, 30-60 minutes before a meal. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks, depending on laboratory blood parameters. The drug is contraindicated in hemochromatosis and non-iron deficiency anemia.
- Iron gluconate - appointed 1 hour before a meal, 0.6 grams per reception, by mouth. In just a day, the patient takes the medicine three times. The course of treatment is 3-6 months. Contraindicated in skin porphyria, hemochromatosis, anemia, not associated with a deficiency of iron ions.
- Iron chloride - taken orally between meals, 2 drops per reception. The course of treatment is two months. Contraindications do not differ from those for the two drugs described above.

The effect of treatment with ferrous iron preparations becomes noticeable on the 10-12th day of therapy, when the level of reticulocytes rises. An increase in hemoglobin concentration is noted by the end of the 3rd week. The level of 120 grams per liter is reached in about a month and a half. After this, the tablets continue to be taken for another 1-2 months.
Ferric preparations
Ferric iron preparations have a slightly lower bioavailability than their divalent species. This is due to the fact that the body is able to absorb only the nutrient in the divalent version. Ferric iron that has entered the bloodstream is first converted to ferrous iron, after which it is absorbed by the above mechanism. Trivalent drugs are available both in parenteral dosage forms, and in the form of tablets, syrups, drops.

- Ferrum Lek - the drug is available in injectable form, contains ferric iron. 2 ampoules are prescribed 2 times a week with intravenous administration and 2 ampoules every other day with intramuscular administration. The course of treatment is 1 month.
- Ferrocene - bitter crystalline powder of dark red color. Easily absorbed from the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, is used to treat iron deficiency anemia. In tablet form, the medicine is taken at 0.3 grams three times a day, preferably after a meal. The course of treatment is 30 days.
- Maltofer - Available in the form of chewable tablets. The drug is taken 1 tablet 3 times a day. Treatment takes about 3-5 months. Unlike previous tablet preparations, the maltofer tablet can be chewed.
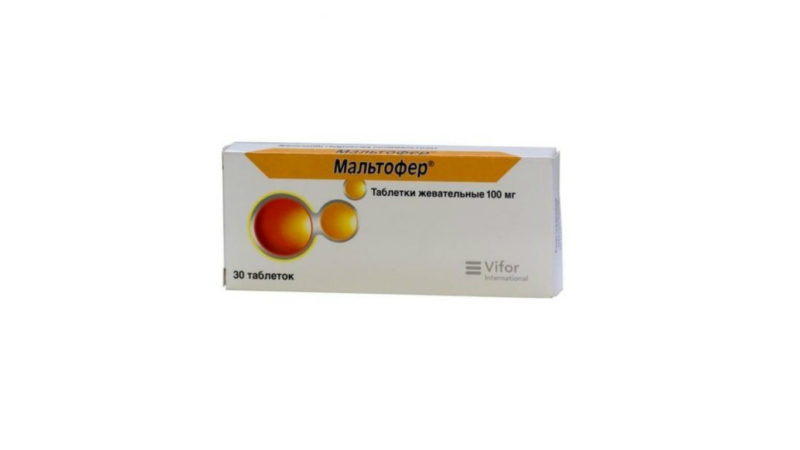
In combination with iron preparations, ascorbic or folic acid is usually prescribed to the patient. It is impossible to use drugs at the same time as eating foods containing a large amount of protein. This leads to the binding of the nutrient to food proteins and the leveling of the therapeutic effect of the drug.
Note: preparations intended for enteral use can cause darkening of tooth enamel. Therefore, after taking them, it is recommended to brush your teeth. The tablets, with the exception of chewable ones, are swallowed whole without chewing.
Iron Injections
In the form of injections, mainly preparations based on ferric iron are produced. These include ferrum lek, ferbitol, fercoven. Intravenous administration of drugs of this group is extremely rare, since there is a high risk of allergic reactions of the immediate type (anaphylactic shock, angioedema). Intramuscular administration is safer.
Drugs are injected into a vein at a dilution with physiological saline. The rate of administration does not exceed 50 mg / min. The administered dose is increased smoothly, bringing it to therapeutic within a few days. The frequency of administration of intravenous forms is 2 injections per week, parenteral - every other day. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks. The average therapeutic dose for adults is 100 mg per administration.
Three days before the intended start of the introduction of parenteral forms of iron-containing agents, its tablet forms are completely canceled. Otherwise, plasma oversaturation with metal ions is possible. A component that is not bound by ferrotransferin protein remains in a free state and has a toxic effect.
Note: Dosage forms for intramuscular and intravenous administration are not interchangeable! It is forbidden to use a drug intended for introduction into the muscle for intravenous administration. The converse is also true.
Vitamins and dietary supplements for raising hemoglobin
Vitamins themselves are not able to compensate for the lack of iron. However, they can be used so that preparations based on the necessary element are better absorbed. Accelerate the cure of the disease with the help of vitamins "C", "B", folic acid.It is best to take vitamins as part of multivitamin complexes intended for the treatment and prevention of iron deficiency anemia. Among these complexes is nutrimaxvision, vitabioticsferoglobin.

To increase the level of hemoglobin, dietary supplements, biologically active additives based on plant materials can also be used. The funds of this group are usually positioned by the manufacturer as highly effective, but it should be remembered that the content of active substances in them is lower than in full-fledged drugs. In addition, some dietary supplements are essentially a placebo (blende) that does not have any therapeutic effect. Among the additives are hemobin, pantohematogen and others. Before using them, consult your doctor.
Features of the choice of medicines
At the beginning of iron therapy, a choice should be made in favor of trivalent agents intended for oral administration. Medicines in this category are highly effective in combination with ease of use. There is no need to strictly observe the time intervals between meals and tablets, as is the case with divalent drugs.
Divalent iron preparations are obsolete, but have a lower cost. Therefore, their use is justified with a low level of financial security of the patient. Also, drugs are prescribed for people with high acidity of gastric juice. Concentrated hydrochloric acid disrupts the absorption of ferric iron, therefore, funds based on it are contraindicated in such patients.
Parenteral forms are prescribed only when the absorption of drugs from the gastrointestinal tract is impossible (inflammatory diseases, removal of part of the stomach or intestines). In this case, use forms for introduction into the buttock. Intravenous varieties of iron-containing drugs are prescribed strictly according to indications, with a critical decrease in hemoglobin and iron in the blood plasma. Often this is combined with blood transfusion (blood transfusion).
Differences between children and adults
Iron deficiency anemia in adults and children is treated using the same drugs. There are differences in dosage. The amount of active substance for the treatment of pediatric patients is reduced by three times relative to adult therapeutic regimens. In addition, pediatricians try to use dosage forms convenient for children (syrups, chewable tablets).
Iron therapy today is the main treatment for iron deficiency anemia. In the vast majority of cases, replenishment of iron deficiency in combination with elimination of the pathways for nutrient loss leads to a complete recovery of the patient within a few months. However, improper use of drugs can cause severe intoxication and iatrogenic diseases. Therefore, the independent use of iron tablets is unacceptable. Therapy should be prescribed by a doctor with the necessary knowledge and skills. Self-medication is not permissible.