Chickenpox or chicken pox (Varicella zoster virus) is an acute infectious process caused by type 3 herpes virus. Most people suffer this disease even in childhood, after which they develop stable immunity for many years, and cases of re-infection are extremely rare. But an adult, who had not previously had chickenpox, can “catch” the infection by contact with the carrier of the virus. Consider the symptoms and signs of chickenpox, possible complications and preventive measures.
Material Content:
How chickenpox begins in children and adults
If you do not know how chickenpox begins in children and adults, you can confuse it with SARS, and sometimes with intestinal upset.
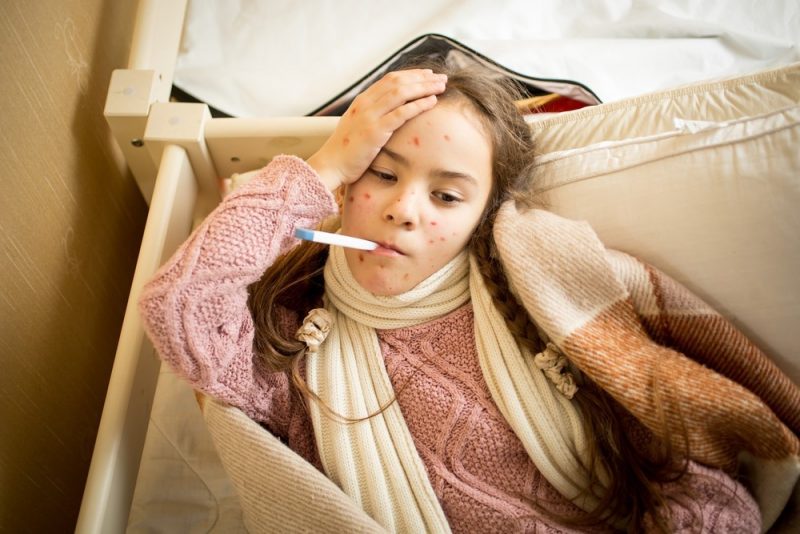

The onset of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness of the mucous membrane in the mouth;
- a slight increase in temperature;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- lack of appetite;
- cutting pains in the stomach;
- sometimes - stool disorders, nausea and vomiting.
Rashes on the skin do not appear immediately, this can happen three weeks after the infection enters the body. But a person can already infect others at the initial stage of the disease, it is transmitted by airborne droplets. Moreover, the chickenpox virus is characterized by unprecedented mobility and is able to move through the air by 20-25 m.
Incubation period
The duration of the incubation period of chickenpox in adults and children depends on the immune activity of the body and can be from 5 to 21 days after contact with the virus carrier.
After infection in the respiratory organs, the pathogenic microflora is fixed in the mucous membranes and begins to multiply intensively. At this stage, there are no signs of the disease, a person can feel only a slight malaise, which, as a rule, does not attach particular importance.
For some time, viral bodies accumulate, and after reaching a certain concentration, they enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, affecting to a greater extent lymphatic fluid, epithelial cells and mucous membranes. The disease passes into a new stage, the incubation period ends, and the first signs of chickenpox appear.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
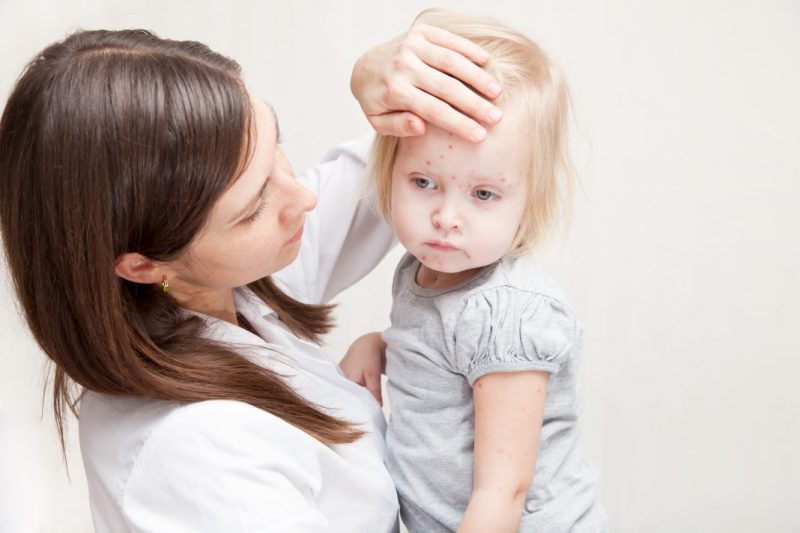

Symptoms of chickenpox depend on the stage of the disease. If at first it makes itself felt with a slight malaise, then after one or two days the following manifestations occur:
- a sharp increase in body temperature, sometimes up to 40C;
- headaches, mainly in the forehead and temporal regions;
- muscle spasms;
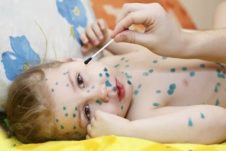
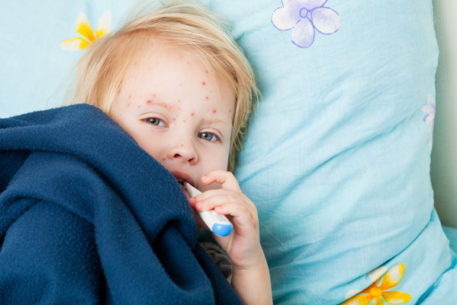
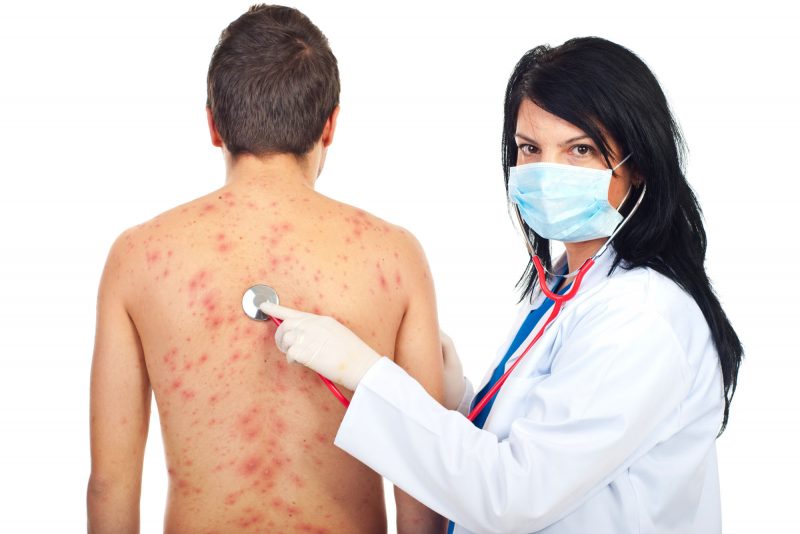
- rash in the form of bright red bubbles filled with a clear liquid;
- itchy skin.
As a rule, at first small pimples form on the face of a child or adult, and then quickly spread over the entire surface of the body. Sometimes it takes no more than a few hours. In addition, in older people, almost always, in addition to the skin, the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth and genitals are affected. This is accompanied by severe itching, which can be somewhat alleviated by treating the rash with brilliant green or fucorcin.
After a few days, the clear liquid in the pimples darkens, after which they burst. A crust forms at the site of the lesion, which subsequently disappears.
Attention! In no case should you scratch the rash or tear off the crusts, as this can lead to infection in the wounds, which will significantly complicate the course of the disease. In addition, scars in the form of round indentations may remain on the skin.
How many days does chickenpox last
How long chickenpox lasts depends on the form of the disease. The acute stage, which is characterized by a rash and ends when new pimples no longer appear, are classified as follows:
- Easy, when the patient has a slight increase in temperature, and rashes are not plentiful. In this case, the acute process will last from 2 to 3 days.
- Medium, proceeding against a background of high temperature, with a rash covering most of the body. With this form of the disease, the stage of rashes will take at least 5-7 days.
- Severe, which is characterized by fever and abundant rashes not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. And also a similar form of chickenpox is accompanied by severe head and muscle pain, sore throat and intolerable itching. In this case, the acute stage will stretch for 7-14 days.
On average, chickenpox lasts about 20 days. In this case, the patient presents a danger not only in the acute stage of the painful process, but also within a week after the rash disappeared and the last crust disappeared. To prevent the spread of infection, during this period, an infected person should not contact with others.
Possible complications and consequences
Almost always, children tolerate chickenpox quite easily, the disease disappears against a background of a slight increase in temperature and mild respiratory symptoms, while the rash affects only some parts of the body.
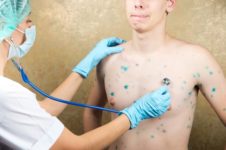
Complications arise if the herpes simplex virus type 3 affects an adult or an infant, as well as in cases of atypical course of chickenpox. With these forms of infection, pathogenic microorganisms affect cells of various organs, causing disruptions in their work.
This threatens the development of the following dangerous consequences:
- tinea versicolor;
- epilepsy;
- inflammation of the meninges (meningitis and encephalitis);
- pneumonia and other respiratory problems;
- visual and hearing impairment of varying severity;
- lesions of the liver;
- paresis of limbs;
- paralysis.
With malignant forms of chickenpox, the probability of death reaches 25%. This happens if, as a result of the disease process, severe, irreversible disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems have occurred. Most often, chickenpox occurs in a similar way in patients of infancy and senility, as well as in individuals with weakened immune defenses.
In other words, the outcome of the disease and the likelihood of complications depend on many factors. These include the form and severity of the disease, the age and individual characteristics of the patient.
Preventive measures
The insidiousness of the herpes simplex virus type 3 is that it is almost impossible to defend against it. Chickenpox is extremely contagious, and you can get sick not only in case of direct contact with the peddler of its pathogen, sometimes pathogenic bacteria penetrate the body and through household items. For example, if a healthy person used the same dishes with a sick person.
Therefore, patients with chickenpox are recommended to be isolated from others, but these measures are not always effective, since carriers of the virus are sources of infection even before the disease begins to manifest itself.
Since 2008, Russia began to use the chickenpox vaccine, but so far it has not been included in the list of compulsory vaccinations.
Carry out this procedure according to the following scheme:
- patients from 2 to 13 years old - once;
- adolescents from 13 years old and adults who were not sick people - twice, with an interval of 60-75 days.
And also with the help of these drugs, you can conduct emergency vaccination. This is done within 4 days after the patient was in contact with the carrier of infection.
About a week after the composition is administered, the child or adult may experience symptoms such as a slight malaise, fever, or a few rashes. This is not a cause for concern and is not considered a complication requiring special treatment, in a few days everything will go away by itself.
Opinions of experts regarding whether to be vaccinated against chickenpox differ. Some believe that vaccination is necessary, but according to others, such a measure can lead to serious complications. Therefore, the decision on the need for this procedure should be made by each patient independently, aware of the potential risks.