"Sumamed" (suspension for children) is used for antibiotic therapy. Specialists prescribe the medication according to the instructions for use, but the dosages in each case differ, depending on the individual characteristics of the child's body.
Material Content:
- 1 Release form, composition (active substance)
- 2 Pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics
- 3 What is prescribed Sumamed suspension?
- 4 At what age can an antibiotic be given
- 5 Instructions for use and dosage for children
- 6 Powder for oral suspension
- 7 Drug Interactions with Other Drugs
- 8 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 9 Antibiotic Analogs
Release form, composition (active substance)
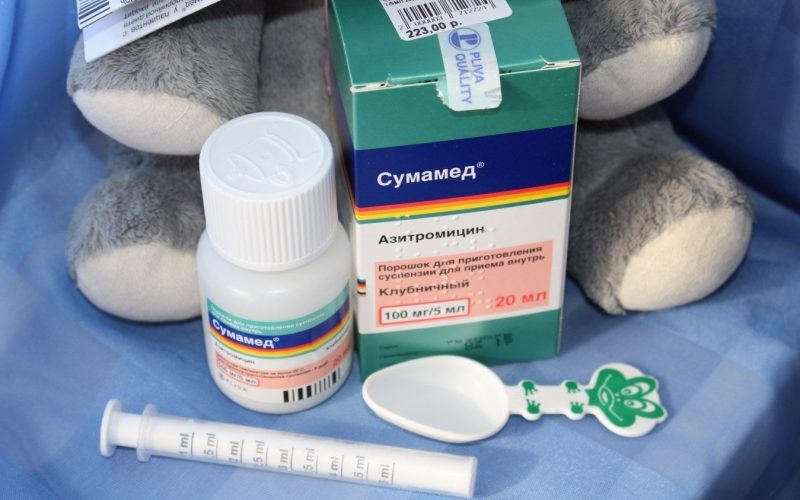
The pharmacological agent is implemented in the form of a powder composition intended for the manufacture of a suspension (21 g in one bottle). One package contains a container with powder, a measuring spoon and a detailed instructions for use.
The powder for the preparation of a suspension in a suitable state is yellow and has a light berry aroma.
One bottle with a pharmaceutical product is enough to make 20 ml of the finished antibiotic. The active substance azithromycin in the resulting solution is contained in a dosage of 100 mg / 5 ml.
The composition of the antimicrobial medication, in addition to the active substance, includes other components responsible for the preservation of the drug and the formation of its dosage form.
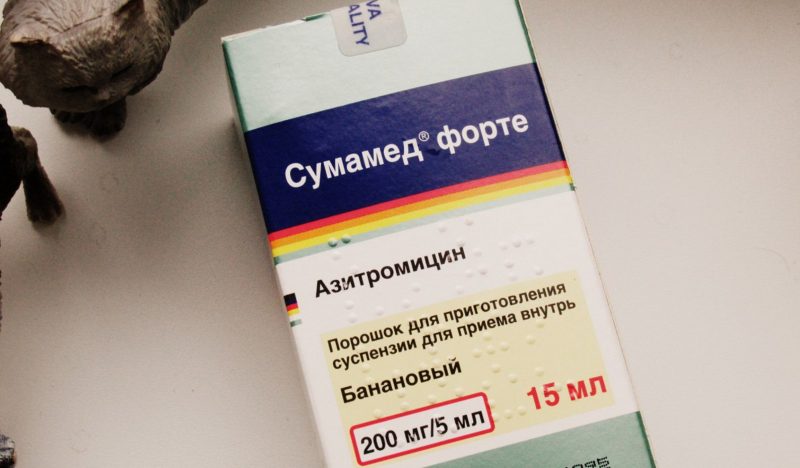
Also on sale is the drug "Sumamed Forte." Its difference lies in a higher dosage of the active ingredient in the finished solution.
Pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics
The drug in question is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. After use, the medication is rapidly distributed throughout the body through the circulatory system.
The antibacterial component seeps through the cell membrane into the phagocytes and moves to the site of infection. Thus, its maximum concentration is located directly at the site of damage by pathogenic microorganisms and is observed 12 to 72 hours after administration.
Withdrawal of the drug from the body occurs within 76 hours. Such a long period allows the use of medication no more than 1 time per day. To suppress most infections, you only need to take a three-time medication.
The breakdown of the substances that make up the suspension occurs in the liver. From there, they are excreted with bile unchanged. There is also a slight excretion of the pharmaceutical with urine.
What is prescribed Sumamed suspension?
Children's "Sumamed" allows you to suppress the pathological processes and reactions that develop as a result of the activity of bacteria that are sensitive to the active substance of the drug.
So, indications for use are:
- bacterial diseases of the respiratory system;
- hearing anomalies of a bacterial nature;
- pneumonia
- bronchitis of various etiologies of acute or chronic course;
- gastrointestinal ulcer of a bacterial nature;
- moderate acne;
- bacterial damage to the skin or muscle fibers;
- Lyme borreliosis in early diagnosis;
- urinary tract infection with chlamydia.
Specialists can also prescribe an antimicrobial medication in situations not described in the instructions.
At what age can an antibiotic be given
- The Sumamed suspension for children with antibacterial action is allowed for the treatment of young patients who have reached six months. At the age of over three years, the volume of one bottle is not enough to undergo a full course of treatment.
- The Sumamed Forte suspension (200 mg / 5 ml) is used in the treatment of children from six months if their weight exceeds 10 kg. The tool can be used up until the moment when such a form is convenient.
Instructions for use and dosage for children
Experts recommend taking the medication one-time during the day in between meals. It is optimal to take 60 minutes before eating or after a couple of hours. The drug must be washed down with a sufficient amount of liquid so that its remains do not remain in the oral cavity and on the walls of the throat.
Mixing the medicine with water or other fluids is strongly discouraged.
- For the treatment of bacterial damage to the organs of hearing and breathing, as well as soft tissues, it is necessary to take 10 mg of the active substance per 1 kg of the body weight of the child. The duration of therapy is 3 days. For a child weighing 5 kg, 2.5 ml of suspension is required. For each subsequent kilogram of weight (up to 10 kg), 0.5 ml is required to be added.
- In case of damage to the respiratory system by streptococcal infection, it is recommended to take 20 mg of the drug per 1 kg of the child's weight 1 time per day. The duration of therapy is 3 days. The maximum allowable dosage is 500 mg per day.
- When diagnosing tick-borne borreliosis, it is recommended to use an antibacterial drug according to the following scheme: 1 day - 20 mg per 1 kg once every 24 hours, and from 2 to 5 days - 10 mg per 1 kg once every 24 hours.
Changing the presented dosages in children with small abnormalities of the kidneys and liver is not required. But before implementing treatment, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
If the next use of the medication was not carried out on time, you should drink the prescribed dosage immediately after identifying the problem and continue taking it according to the schedule prescribed by the specialist with an interval of 24 hours.
Before each use, it is recommended to shake the contents of the vial with the antibacterial agent, since a suspension with the active component settles in it. If the product is used twice (for example, for different children) with a break of more than 20 minutes, it is necessary to re-mix the contents of the bottle.
It is recommended to measure the required amount of a pharmacological agent with a measuring syringe or a spoon, on which the volume of the substance collected is indicated. After use, the appliance used must be thoroughly rinsed and dried. Storage of measuring accessories is recommended to be carried out in a dry place, protected from dirt and dust.
Powder for oral suspension
To prepare a children's antibiotic, 12 ml of clean, cold water is required to be introduced into a bottle with a dry composition inside. It is recommended to measure the liquid with a measuring syringe in order to accurately comply with the dosage of the finished product.
The medication will turn out more than stated on the package. Excessive amount compensates for the amount lost during the dosage of the drug.
It is permissible to store the prepared suspension in cool for no longer than 5 days from the date of preparation.
Drug Interactions with Other Drugs
- Alcohol and medicines with its content significantly increase the effect of azithromycin and increase its concentration in the blood.
- Medicines aimed at lowering the acidity in the stomach contain magnesium and aluminum. These components interfere with the absorption of the antibiotic. Reception of the described pharmacological agents should be alternated with an interval of 1 hour.
- "Warfarin" is not recommended for use simultaneously with an antibacterial drug. If there is an urgent need for co-administration of drugs, the patient should be carefully monitored.
- Tetracycline drugs significantly increase the effect of azithromycin on the body. Their combination is extremely undesirable. The minimum interval between doses of these drugs is 3 to 4 hours.
- The simultaneous use of Sumamed and antacid drugs is prohibited, as this leads to impaired absorption of azithromycin, which entails a weakening of the therapeutic effect. The minimum interval between taking medication is 4 hours.
- The combined use of an antibacterial and ergot alkaloids increases the risk of developing intoxication of the body.
- It is forbidden to use several antibiotics from the macrolide group. Their combination enhances the severity of negative manifestations and can provoke serious consequences.
Many drugs enter a direct reaction with azithromycin, which can adversely affect the condition of the child. If you need to use different medicines together, you should consult with a specialist.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
It is forbidden to use the medication with individual intolerance to the components that make up its composition, as well as with severe diseases of the urinary system and liver.
Caution should be taken to use an antibiotic to treat newborns, as well as pregnant and lactating women.
The following adverse reactions may occur from taking the drug:
- allergic manifestations;
- nephritis;
- thrush in the intimate area;
- violation of the digestive tract;
- pathological changes in the rhythm of the heartbeat;
- pain in the area of the heart muscle;
- sleep disturbance;
- Anxiety
- hypersensitivity to ultraviolet rays.
With excessive use of the antibacterial drug, the child may experience attacks of nausea and vomiting, as well as diarrhea. In rare cases, partial or complete hearing loss for a short time is possible.
If such manifestations are detected, experts recommend symptomatic therapy.
Antibiotic Analogs
In pharmacy chains, various drugs containing azithromycin are sold. Their average cost varies from 30 to 400 rubles, depending on the manufacturer and place of sale.
Scientific studies have revealed that drugs with a higher cost have a smaller number of negative manifestations, since the instructions are strictly followed during their manufacture and the components included in the composition are cleaned more thoroughly.
Recommended analogues:
- "Azithromycin" in suspension. The implementation of the medication is in the form of a powder for the preparation of syrup. The pharmacological agent is diluted according to the recommendations on the package and is used in the dosage prescribed by the pediatrician. The average cost of a medication is 250 rubles. Each package contains complete instructions for use.
- "Azitroruss". The cheapest analogue of the drug in question. Its implementation is in the form of a powder for the manufacture of a suspension. The dry preparation is in paper sachets, each of which contains the amount of active substance necessary for the preparation of a single dose. The average cost of one package with 5 bags is 50 rubles.
- "Azitroks". A pharmacological agent can fully replace the drug in question. It is dispensed in powder form for the manufacture of a suspension. One package includes a plastic container with an active component, a spoon for proper dosing and detailed recommendations for use in printed form. In 5 mg of the finished suspension, 200 mg of the active ingredient is present.
Antibacterial therapy is performed under the supervision of a pediatrician. Self-administration of drugs can lead to unpleasant consequences and even death of the child.