Stopping bleeding (hemostasis) is a vital ability of the body. In case of damage to small vessels, it is provided by special blood cells - platelets. In a healthy person, their amount in the blood can slightly decrease and increase. But a significant fluctuation in platelet concentration is always associated with pathology. How thrombocytopenia develops, what it is and how to correct it, is described in the material below.
Material Content:
What is thrombocytopenia?
In the red bone marrow, the normal process of platelet formation is ongoing. Each such element lives on average 8 days, after which it independently collapses in the spleen. The cyclicity and coherence of the formation and destruction of platelets ensures their constant concentration in the blood.

Thrombocytopenia is a pathological decrease in platelet count.
With their deficiency, the primary platelet plug is poorly formed, covering the damaged peripheral vessel, and stopping the bleeding is difficult.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
Thrombocytopenia develops with any violation of the processes of formation and destruction of platelets, as well as their distribution throughout the bloodstream.
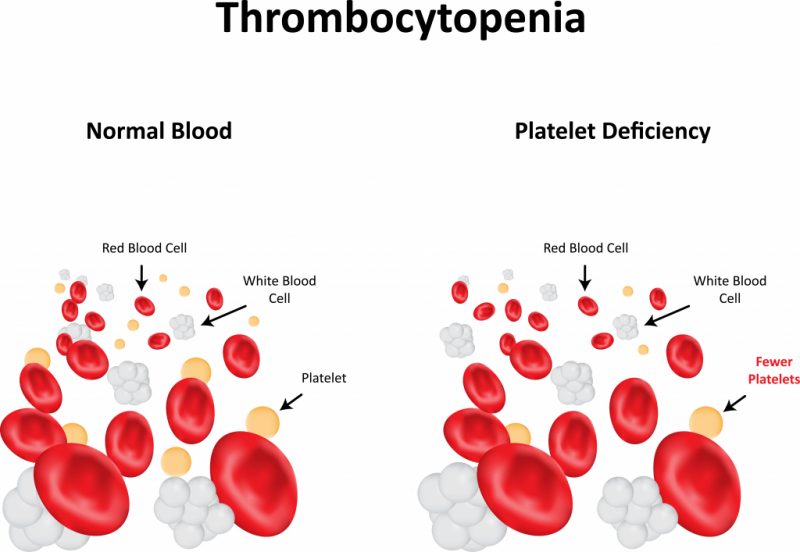
Based on this, a drop in platelet levels in the blood is associated with three main reasons:
| Cause of thrombocytopenia | Pathogenesis Options |
|---|---|
| Decreased platelet production | • Red bone marrow produces few megakaryocytes - the cells from which platelets are produced.This often occurs with bone marrow hypoplasia and is accompanied by a simultaneous drop in the production of other blood cells - red blood cells and white blood cells. • There are enough megakaryocytes, but platelet production is not effective due to a lack of thrombopoietin (a special hormone). It develops with megaloblastic or iron deficiency anemia, alcoholism, severe viral infections or with a number of genetic pathologies. • Megakaryocytes are reborn as a result of cancer, replacement by fibrous tissue or granulomas. Platelet production stops. |
| Platelet destruction acceleration | • Impaired immune mechanisms cause the production of various platelet-destroying antibodies. It can develop with Rh conflict during pregnancy, with blood transfusions, lymphocytic leukemia and lymphogranulomatosis, Evans-Fisher syndrome, autoimmune diseases, viral infections. Sometimes provoked by the use of certain drugs. • Platelets quickly disintegrate when the inner lining of the vessels is disturbed. This occurs with atherosclerosis, heart defects, metastatic lesions or as a result of medical manipulations - bypass surgery, installation of artificial valves. |
| Inappropriate platelet distribution | Most platelets do not circulate through the bloodstream, but linger in the spleen. The condition occurs with portal hypertension, a number of infections (tuberculosis, malaria), leukemia and lymphomas. |
In addition, temporary thrombocytopenia occurs when a large volume of blood is lost or after prolonged exposure to droppers.
A drop in platelet count is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nosebleeds;
- heavy prolonged menstruation and intermenstrual bleeding;
- bleeding gums;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage;
- bleeding in the stomach, intestines and other internal organs.
Similar manifestations can occur against the background of other diseases that are not associated with a decrease in the number of platelets. Therefore, a diagnosis is possible only after laboratory blood tests.
Classification and degrees of thrombocytopenia
Classifications of thrombocytopenia for reasons of occurrence are supplemented by a division into primary and secondary forms.
The primary ones include independent pathologies:
- Vergolf's disease;
- congenital and hereditary diseases of the bone marrow;
- post-transfusion thrombocytopenia after blood transfusion.
Secondary is a significant decrease in platelet count as a result of other pathologies.
Depending on the degree of reduction in the number of platelets, there are three degrees of severity of thrombocytopenia:
- moderate - concentration from 50,000 to 150,000 units per microliter;
- average - concentration from 30,000 to 50,000 units per microliter;
- heavy - concentration below 30,000 units per microliter.
Mild thrombocytopenia can occur subclinically, i.e., almost asymptomatically, manifested only by profuse menstruation or a tendency to nosebleeds. To a moderate degree, numerous point hemorrhages under the skin or in the mucous membranes become noticeable. In severe cases, bleeding develops in the internal organs.
Pathology during pregnancy
A slight decrease in platelet concentration during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, is a normal physiological process. Partly it is caused by hormonal changes, partly by an increase in the volume of circulating blood.

The reason for the excitement is the drop in platelet levels below 100,000 units per microliter.
In such a situation, the doctor’s task is to analyze and eliminate the possible causes of thrombocytopenia:
| Cause | Associated risks | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Immune associated with the production of platelet-destroying antibodies | • utero-placental insufficiency; • hypoxia and malnutrition of the fetus; • thrombocytopenia, bleeding and brain hemorrhage in the fetus; • intrauterine death of the fetus; • severe bleeding during childbirth. | • administration of glucocorticosteroids; • the introduction of human immunoglobulin; • in severe cases - the use of blood products and a recombinant coagulation factor; • in extremely severe cases - removal of the spleen. |
| Symptomatic associated with other pathologies or infections | • miscarriages and premature births; •anemia; • hypoxia and malnutrition of the fetus; • large blood loss during childbirth. | • treatment of the underlying disease; •balanced diet; • preparations of vitamins and folic acid. |
| Non-immune associated with pregnancy pathologies (preeclampsia, preeclampsia, eclampsia). | • miscarriages and premature births; • placental abruption; • edema, hemorrhage and convulsions; • hypoxia and malnutrition of the fetus; • large blood loss during childbirth. | • elimination of the main pathology of pregnancy; •balanced diet; • preparations of vitamins and folic acid; • in severe cases - early birth. |
Since thrombocytopenia during pregnancy can potentially lead to very serious consequences, it is not worth neglecting routine blood tests.
The standard donation of blood from a finger at 10, 20, 30 and 38 weeks of gestation helps to control not only the level of platelets, but also the concentration of hemoglobin, the volume of red blood cells and the general condition of the woman’s immune system.
Survey methods
Thrombocytopenia is confirmed only by laboratory tests. Therefore, if a disease is suspected, the doctor, first of all, gives a referral for tests:
| Analysis Name | The essence of the method | Purpose of |
|---|---|---|
| General blood analysis | Blood taken from a finger is examined in a hematological analyzer and visually under a microscope. | Counting platelet count and other blood elements per 1 microliter. Visual assessment of the morphology of blood cells. |
| Duke's test | A 4 mm puncture is made with a Frank needle or a disposable lancet in the finger, and the time until the bleeding stops is detected. | Determination of bleeding and blood coagulation time. |
In some cases, additional studies are required to clarify the type of thrombocytopenia - immunological tests and bone marrow puncture.
Thrombocytopenia treatment
The treatment of thrombocytopenia is within the purview of a hematologist. A moderate decrease in platelets, as a rule, does not need medical correction. Pathology of moderate severity is treated on an outpatient basis, but severe thrombocytopenia requires mandatory hospitalization.
Drug therapy
The following drugs can be prescribed for the treatment of thrombocytopenia:
| Drug name | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prednisolone | Autoimmune and immune forms of thrombocytopenia. | • infections, mycoses and helminthiases; • gastrointestinal ulcer; • HIV and AIDS; •diabetes; • hypo- and hyperthyroidism; • liver and kidney dysfunction; • lymphadenitis; •osteoporosis; •obesity; •glaucoma; • pregnancy and lactation. | 4 tablets of 5 mg 3 times a day for a month |
| "Intraglobin" | Autoimmune and immune forms of thrombocytopenia. | • individual intolerance. | 5 days intravenous administration based on body weight |
| Etamzilat | All forms of thrombocytopenia, including with unspecified etiology | • thrombosis and thromboembolism; • individual intolerance. | 1-2 tablets 250 mg 3 times a day. |
| Revolade | All forms of thrombocytopenia, including with unspecified etiology | • the presence of risk factors for thromboembolism; • individual intolerance; • with caution - during pregnancy lactation. | 1 tablet of 50 mg or 2 tablets of 25 mg once a day. |
| "Depo-checker" | Large blood loss during menstrual bleeding with thrombocytopenia | •mammary cancer; • severe liver dysfunction; •pregnancy. | Intravenous or intramuscular administration according to an individual scheme |
The listed drugs have complex mechanisms of action and in no case can be used without a doctor's prescription.
The treatment of thrombocytopenia should be monitored by a specialist, as emergency surgery may be necessary if the condition worsens.
Folk remedies
The most popular alternative treatment for thrombocytopenia is nettle broth. Its effectiveness has been proven, which allows you to adjust the mild degree of pathology.

To prepare and use a nettle broth with a low platelet count should be as follows:
- brew 1 cup boiling water 1 tablespoon of dry leaves;
- hold in a water bath for 10 minutes;
- cool under the lid;
- strain and drink 50 ml before meals for a month.
In addition, you can brew rose hips in a thermos and drink instead of tea, adding honey to taste. Especially useful is the combined use of decoctions of nettle and wild rose with uterine bleeding against a low concentration of platelets in the blood.
Nutrition for pathology

A special diet for the treatment of thrombocytopenia has not been developed, but some products help to slightly increase the level of platelets:
- eggs
- beef liver;
- red meat;
- any fish;
- buckwheat;
- spinach, beets, carrots, bell peppers;
- pomegranate, nuts, bananas.
During the treatment of thrombocytopenia, it is important to grind the products well and process them until soft.
Coarse particles damage the larynx, esophagus, inner lining of the stomach and intestines, which increases the risk of internal bleeding. Alcoholic beverages that inhibit the hematopoietic activity of the bone marrow are completely excluded.
The platelet norm in the blood of women, men, children
The treatment of thrombocytopenia continues until the platelet count stabilizes within normal limits. Its borders are quite wide and determined on the basis of age and gender.
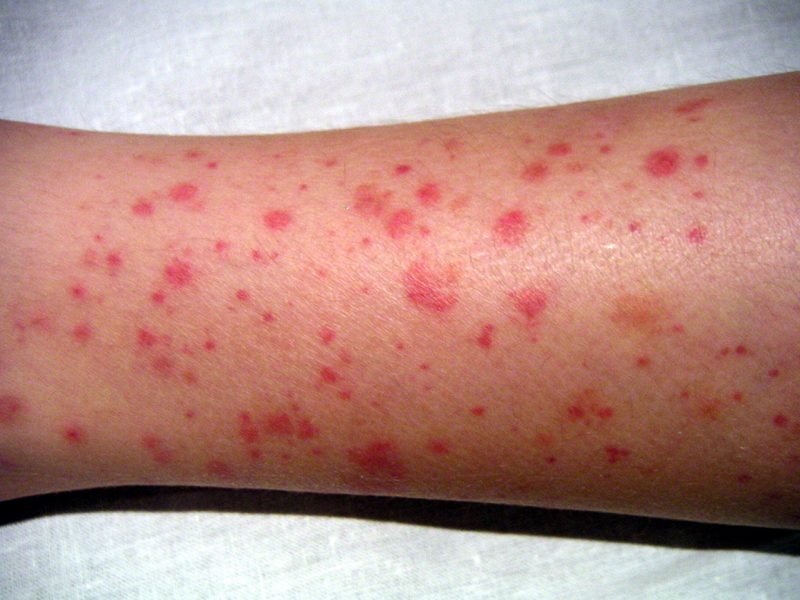
The norm of platelets in the blood of women depends on the current physiological state:
- in the absence of pregnancy and menstruation - from 150,000 to 400,000 units per microliter;
- during pregnancy - above 100,000 units per microliter;
- during menstruation - from 75,000 to 250,000 units per microliter.
The platelet count in the blood of men is more constant and ranges from 180,000 to 320,000 units per microliter.
A drop in indicators is observed only with blood loss or with the development of any pathologies.
Platelet rates in children under one year old are in the range of 180,000-400,000 units per microliter. In children from 1 year to 16 years, normal indicators are from 160,000 to 380,000 units per microliter.
The consequences of thrombocytopenia
The main danger of thrombocytopenia is internal hemorrhage. The most dangerous hemorrhages in the brain or in the retina. In the first case, the case may end in death, and in the second - blindness.
However, with the timely detection of pathology and adequate therapy, the prognosis is quite favorable. If you manage to capture the very beginning of the disease, you can restore platelet count without complications for the body.
It is important to consider that the causes and consequences of low platelets in the blood are closely related.
Thrombocytopenia caused by any other pathology cannot be completely eliminated until the underlying disease has been treated.