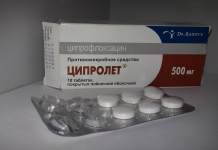
Tsiprolet is an effective antibiotic that helps to cope with various pathologies. It destroys the bacteria that provoke inflammation, and thereby leads to a quick recovery. In order for the effect of therapy to be fully expressed, it is required to clearly follow the instructions attached to the medication.
Material Content:
- 1 Release forms and composition
- 2 Pharmacological action, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- 3 What is the antibiotic prescribed for?
- 4 Instructions for use Cyprolet for children and adults
- 5 During pregnancy and lactation
- 6 Drug Interactions and Alcohol Compatibility
- 7 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 8 Analogues of the drug
Release forms and composition
The chemical compound ciprofloxacin hydrochloride is introduced into the antibiotic. It is it that has the ability to inhibit the activity of bacterial cells.
A medication is produced in the form of tablets for oral administration and subsequent systemic effects on the body. Each dragee is coated with a film membrane for quick swallowing. One tablet contains 250 mg of active ingredient. The package can be 10 or 20 pieces.
Another form of release is eye drops. This is a solution with ciprofloxacin in the composition. 1 ml of a liquid medicine contains 3 mg of the active chemical compound.
As additional ingredients are presented:
- sodium chloride;
- disodium ederat;
- benzoalkonium hydrochloride;
- hydrochloric acid.
The basis of the drug is sterile water for injection.
Pharmacological action, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Tsiprolet tablets are designed to destroy colonies of microbes that have settled inside the body and provoke inflammatory processes.
This is a broad-spectrum drug. It works by inhibiting DNA gyrase in bacteria.As a result, the transfer of genetic material during cell division is disrupted. The consequence of this is the rapid death of a colony of pathogenic microbes.
Tablets are not prescribed immediately. Initially, you need to determine which bacteria have penetrated the body.
The instructions indicate that the drug is active in relation to the following list of gram-negative bacteria:
- Escherichia coli;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Shigella spp;
- Proteus vulgaris;
- Klebsiella spp;
- Citrobacter spp.
The medicine is also used to combat gram-positive microbes, in particular with some streptococci and staphylococci.
An antibiotic enters the bloodstream through the capillaries of the intestinal villi. Further, the compound is uniformly dispersed throughout the tissues and body fluids. Its maximum concentration is observed in blood neutrophils. With plasma proteins, about 30% of the drug received binds.
The half-life lasts 3 to 5 hours. Its duration is determined by the initial state of the kidneys. The spent substance is mainly excreted in the urine and only about 15% - with feces.
What is the antibiotic prescribed for?
All the necessary information about the medicine will be provided by the doctor. In addition, it is required to study the instructions, which indicate how to correctly take Tsiprolet, from which it is usually prescribed, and what may be restrictions.
The list of indications includes conditions provoked by the pathogenic activity of bacteria.
So, an antibiotic is necessary for infections:
- bone tissue;
- Musculature
- skin integument;
- mucous membranes
- ENT organs;
- genital tract;
- kidney and urinary ducts;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory tract;
- the oral cavity.
This list allows us to conclude that the tool is multifunctional. Doctors recommend Tsiprolet for angina, sepsis, peritonitis, cystitis and many other pathologies.
Important. Previously, tests are required to determine whether the existing strain of microorganisms is sensitive to ciprofloxacin. If the bacteria are resistant, you will need to choose a different drug.
Instructions for use Cyprolet for children and adults
The antibiotic "Tsiprolet" is taken strictly according to the scheme developed by the attending physician for a specific case. The dose and duration of therapy depend on the diagnosis.
- With pathologies of the kidneys, bladder and ducts, 250 to 500 mg are taken twice a day. The volume of dose depends on the severity of the symptoms.
- In the treatment of respiratory diseases, the patient is required to take 250 - 500 mg per day. The dose is divided into two doses.
- With gonorrhea, a single dose in the dosage chosen by the doctor (250 - 500 mg) is sufficient.
- With intestinal infections accompanied by diarrhea, it is enough to take 250 mg per day.
- For pathologies associated with an increase in body temperature, 500 mg is prescribed twice a day. The total volume is 1000 mg.
The duration of the course usually varies from 7 to 10 days. It is not advisable to prescribe an antibiotic for less than 5 days, since during this period the colony will not be completely destroyed, and the surviving microbes will become resistant to the drug. For further treatment, you will have to choose a more powerful, and therefore more toxic medication.
Important. For any pathology, the tablets are taken on an empty stomach, not chewing, but immediately swallowing. It is better to do this at the same time at equal intervals, for example, at 8:00 and 20:00 daily.
During pregnancy and lactation
Neither when carrying a child, nor during lactation, you can not take the drug. If there is a need for emergency treatment, you need to consult a doctor and choose a safe analog for the developing fetus or child on natural feeding.
Drug Interactions and Alcohol Compatibility
Antibiotics cannot be combined with alcohol. Tsiprolet was no exception.
Tablets are not recommended to be taken at the same time as alcohol, since such a combination is fraught with undesirable consequences, which include:
- a rapid decline in the effectiveness of the tool;
- excessive load on the liver, the cells of which are involved in the neutralization of alcohol;
- guaranteed development of side effects.
Tablets are undesirable to take in parallel with some other medicines. In particular, co-administration with Cyclosporine enhances toxic effects on the liver. A similar effect is observed when using "Theophylline". The concentration of this drug in serum will increase, and its half-life will become too long. If the patient uses any antacids, then the absorption of the antibiotic will be slower, and its effectiveness will drop.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
You can not prescribe tablets in the following conditions:
- pregnancy;
- breast-feeding;
- hypersensitivity;
- age up to 18 years;
- pseudomembranous colitis.
Doctors also list conditions in which the use of tablets is possible, but the condition of the patient will require increased attention.
This list includes:
- liver pathology;
- renal failure;
- atherosclerosis;
- mental disorders;
- epilepsy;
- elderly age.
During the use of the antibiotic, the patient may develop side effects.
The most common among them:
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- stomach ache;
- the appearance of a rash on the skin.
These signs indicate dysbiosis - a condition associated with imbalance in the microflora in the intestines. The fact is that antibiotics destroy even beneficial microorganisms that are responsible for normal digestion.
To prevent this from happening, in parallel with Tsiprolet, doctors prescribe eubiotics, for example Linex or Acipol.
Other side effects include:
- headache;
- confusion of consciousness;
- fainting
- hearing impairment;
- tachycardia;
- erythema;
- itchy skin;
- urinary retention;
- myalgia;
- general weakness.
All of these symptoms reach their peak intensity with an overdose of the drug. In this case, immediate medical attention will be required. There is no antidote, so the patient will need an urgent gastric lavage and the provision of plenty of water.
Analogues of the drug
Analogs of Tsiprolet may be prescribed by a doctor, not at all inferior to him in effectiveness. The most famous is Ciprofloxacin, which is also available in tablet form.
Other similar medications included:
- Ciprinol;
- Quintor;
- "Tsiloxan";
- "Ecocifol";
- Norfloxacin.
All of the listed medicines, like Tsiprolet itself, are dispensed only with a prescription from the doctor. It is strictly forbidden to prescribe a drug on your own and use it not according to instructions.