Heparin is a direct anticoagulant that prevents the development of thrombosis, blocking blood vessels. Heparin injections are considered the safest and most effective form. Since with the correct dosage, it is possible to avoid side effects that are inevitable during treatment with ointment.
Material Content:
The composition of the drug
Injectable heparin is a colorless liquid that is administered intravenously, subcutaneously. The drug contains the active ingredient heparin sodium, 5000 IU.
Besides him, injections consist of:
- sodium chloride;
- benzyl alcohol;
- water for injection.
A cardboard box contains 10 glass ampoules.
Pharmacological actions, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Instructions for use claims that the active substance successfully eliminates thrombosis, does not allow increased blood coagulation. After penetration into the body, Heparin lowers the amount of cholesterol in the blood. In addition, the drug has a positive effect on the state of plasma, helps to eliminate chylomicrons from the circulatory system.
Important! It is forbidden to use heparin as a drug that lowers cholesterol, in the presence of a predisposition to bleeding.
Heparin injections are prescribed to eliminate factors leading to increased blood coagulation.
The drug, after it reaches the affected area, has the following pharmacological effects:
- does not allow the synthesis of thrombin;
- does not allow blood clotting;
- maintains the necessary level of vascular permeability;
- allows blood clots to naturally dissolve;
- improves blood flow to the myocardium;
- leads to a decrease in cholesterol in the circulatory system;
- does not allow an immune response to an organ transplant;
- reduces the inflammatory process of blood vessels;
- helps to suppress the immune system to combat autoimmune pathology.
The solution for injection begins its effect immediately after penetration into the body. However, the effect of the drug is short-term, not more than 5 hours with intravenous administration. If the injections were given subcutaneously, then the action begins after an hour and lasts about 12 hours. Moreover, heparin changes the composition of the blood, but this process lasts a short period of time. The metabolic process occurs in the liver cells, the active substance is excreted through the urinary system.
Why are heparin injections prescribed?
Heparin injections are prescribed for various diseases.
Usually they are used for the following purposes:
- treatment of thromboembolic pathologies;
- prevention of vascular blockage;
- therapy for thrombosis caused by a heart attack;
- elimination of clots in arteries;
- blood purification;
- treatment of atrial fibrillation;
- treatment of deep vein thrombosis;
- fight against leukoplakia;
- elimination of microcirculation disorders.
On a note! Heparin injections are usually used simultaneously with fibrinolysin. This complex accelerates the anticoagulant effect.
In addition, heparin solution is used to treat venous catheters. The drug is prescribed for patients with cardiac ischemia to prevent acute thrombosis, sudden death, recurrence of a heart attack.
Instructions for use of the drug
The best result is from the intravenous administration of Heparin solution. Thus, a more stable effect appears, which less often leads to such a complication as bleeding. The dose of the drug is calculated individually, taking into account the type of disease and its severity.
On a note! If there is a need for the introduction of Heparin to children, then this process is carried out through a dropper.
Typically, injections are given by a doctor, sometimes at the stage of first aid, as in myocardial infarction. At the initial stage of treatment, the daily dosage is 15,000 units. In a hospital, the dose is usually increased to 40,000 units. The maximum dosage is divided into 4 times, and a 4-hour break must be observed between injections.
Important! During treatment every other day, monitoring of blood coagulation time is necessary. Against the background of therapy, it should not be exceeded by two times the average.
In order to prevent the deterioration of the patient's condition, a gradual withdrawal of the medication should be made. Each injection dose is reduced by 5000, 2500 Units, not allowing an increase in time between intervals. Gradually, anticoagulants of indirect action are introduced into the complex of therapy. After observing the patient, in a stable condition, heparin is replaced by indirect anticoagulants.
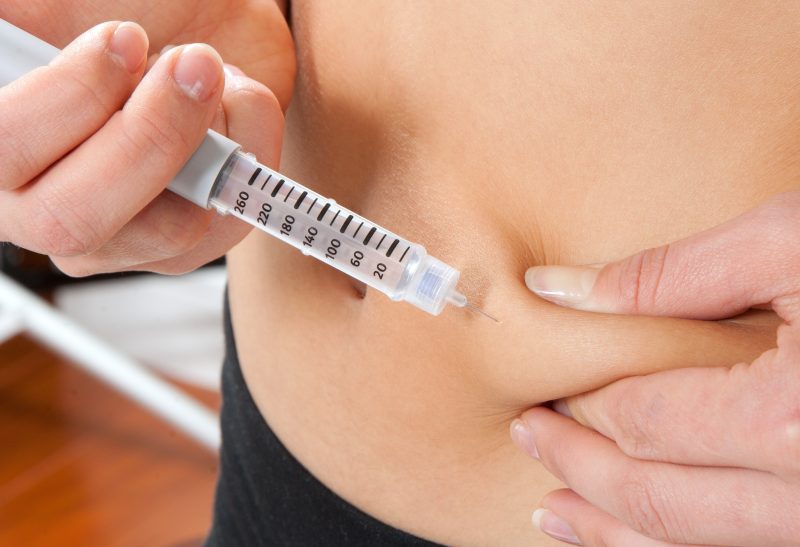
Heparin is often prescribed abdominal injections, for which it is necessary to consult a doctor who will mark the injection site, since in this way self-treatment is most often performed. "Tips" made by a medical professional will help to avoid placing an injection into a vessel (incorrect injection).
Subcutaneous injections are given in the morning or evening, as prescribed by the doctor. Usually, insulin needles are used for the procedure, which are almost not felt and do not cause pain during administration. If there is no way to put an injection in the stomach, then it is possible to introduce it into the thigh, shoulder.
During pregnancy and lactation
If necessary, the appointment of heparin injections during pregnancy is possible. Its active substance does not penetrate through the placental barrier. Thus, the drug does not harm the fetus.It is also possible according to the indications of treatment during breastfeeding. But lactating women are recommended to use the drug in the minimum dose, which gives the necessary result, since the development of osteoporosis, a disease of the spine is possible.
Drug interaction
Heparin injections should be used with caution with certain medications.
Simultaneous use with these groups leads to an enhanced action of Heparin:
- non-steroidal;
- dipyridamole;
- calcium secretion blockers;
- intestinal antibiotics.
The following drug groups weaken the effect of heparin:
- antihistamines;
- alkaloids;
- cardiac glycosides;
- phenothiazine;
- a nicotinic acid;
- nitroglycerine;
- tetracyclines;
- alkaline amino acids;
- protamines;
- thyroxine;
- polypeptides.
A worsening therapeutic effect is also noted if the patient is exposed to smoking.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
Injection heparin has fewer contraindications than local use.
Nevertheless, the drug is not indicated for use in the following conditions:
- slow blood coagulation;
- increased vascular permeability;
- predisposition to internal bleeding;
- renal failure;
- serious liver damage;
- inflammatory process of the atria;
- aneurysm;
- leukemia;
- bacterial endocarditis;
- oncological processes;
- decrease in hemoglobin level;
- bone marrow diseases;
- venous gangrene.
Before subcutaneous administration of Heparin, a diagnosis is necessary to eliminate contraindications.
Against the background of prolonged treatment with this drug, the following side effects may develop:
- redness of the skin;
- skin rashes;
- burning sensation;
- itching
- bronchospasm;
- anaphylactic shock;
- internal bleeding;
- lowering of platelet blood;
- headache;
- vomiting
- joint pain;
- increase in blood pressure;
- diarrhea
- lack of appetite.
If long-term treatment was carried out for people suffering from thrombocytopenia, then gangrene, myocardial infarction, calcium deficiency, bone fragility, alopecia can occur. An overdose of the drug is possible, which is manifested by the development of internal bleeding.
Anticoagulant analogues
In view of the large number of contraindications, rather serious side effects, Heparin analogues are often selected.
Typically, the original is replaced with the following injection drugs:
- Clexane is usually used in vascular operations for patients who are lying for a long time to exclude thrombosis;
- Fraxiparin is commonly used in orthopedics and oncology to prevent thromboembolism. There are known cases of using injections for myocardial infarction, angina pectoris;
- Troparin, which is used as a prophylactic for thromboembolism.
Usually, heparin analogues in injections have a higher price. A doctor should select the substitutes to exclude the development of an undesirable reaction from the body.
Heparin in injections is the safest compared to ointment. The drug avoids thrombosis, improves blood microcirculation.